What is Efflorescence
Efflorescence is a whitish crystalline deposit on surface of the bricks. Usually magnesium sulphate, calcium sulphate and carbonate of sodium and potassium are found in efflorescence. The movement of groundwater into the foundations of buildings and by capillary action into brickwork is very often the cause of efflorescence.
Remedies of efflorescence
- Well fired bricks should use for construction.
- Sand testing should done before starting construction work.
- Proper DPC should provide in building.
- Efflorescence should be remove by dry brushing and washing repeatedly. These efflorescence may reappear in dry season but are in less intensity.

Procedure for Testing Efflorescence of bricks
Apparatus Required
- A shallow flat bottom dish containing sufficient distilled water to completely saturate the specimens. The dish shall be made of glass, porcelain or glazed stoneware and of size 180 mm x 15O mm X 40 mm depth for square shaped and 200 mm diameter X 40 mm depth for cylindrical shaped.
- Distilled water
- Brick specimens
Test Procedure
- Fill distilled water in shallow dish and place one end of brick in dish. Water should fill in dish such that bricks should immersed in water up to 25 mm depth.
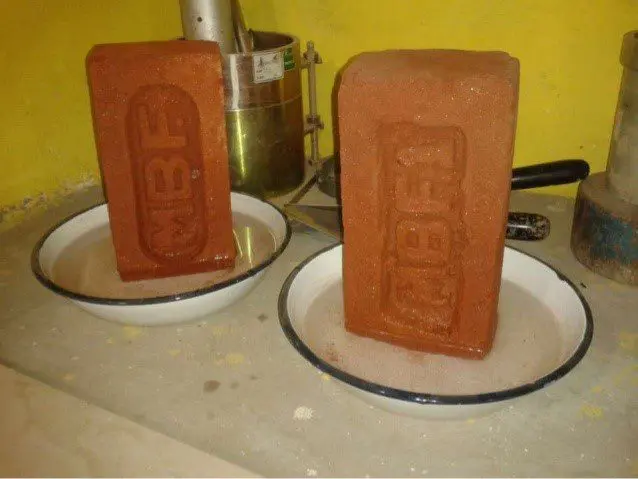

- Place this whole arrangement in a warm ventilated room such that whole water is absorbed by the specimen and the surplus water will get evaporated.
- Cover the dish containing brick with suitable glass cylinder so that there will not excessive evaporation from dish.
- When whole water get absorbed and brick appears to be dry, place a similar quantity of water in the dish and allow it to evaporate as before.
- After this process examine the bricks for efflorescence and report results.
Results of Efflorescence test
Results of efflorescence test shall be reported as nil, slight, moderate, heavy or serious.
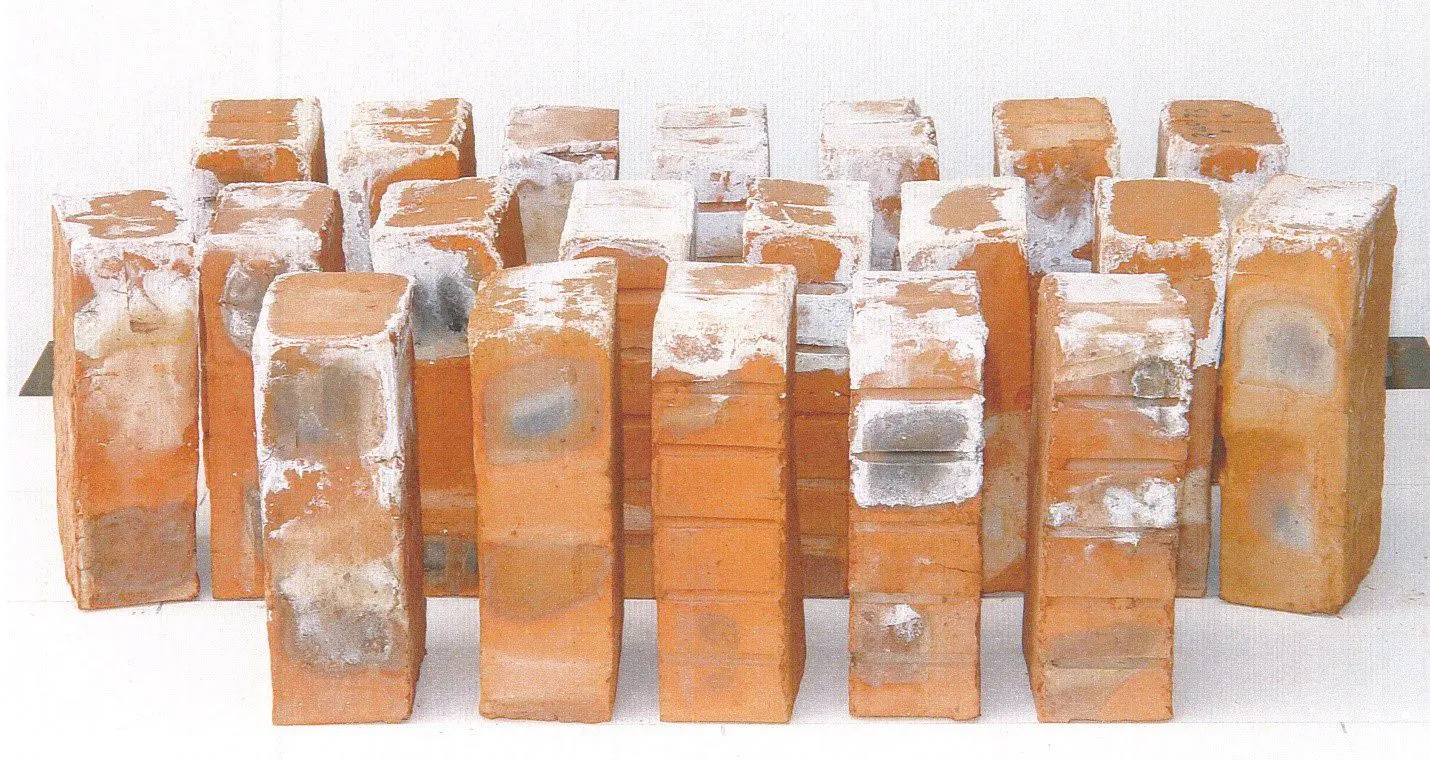

- Nil- If there is no noticeable deposit of efflorescence.
- Slight- when less than 10% of exposed area of brick is covered by a thin layer of salt.
- Moderate- When there is a heavier deposit than under ‘slight’ and covering up to 50 percent of the exposed area of the brick surface but unaccompanied by powdering or flaking of the surface.
- Heavy – When there is a heavy deposit of salts covering 50 percent or more of the exposed area of the brick surface but unaccompanied by powdering or flaking of the surface.
- Serious-when there is heavy deposit of salt acquired by powdering and/or flaking of exposed surface.