Redefining Fenestrations
Fenestrations are basically the required transparency on a façade to attach ourselves with the external environment or the exterior world. They play a dual role of bringing the out in and the in out. The process has a similar function but a lot many ways to bring this process in action.
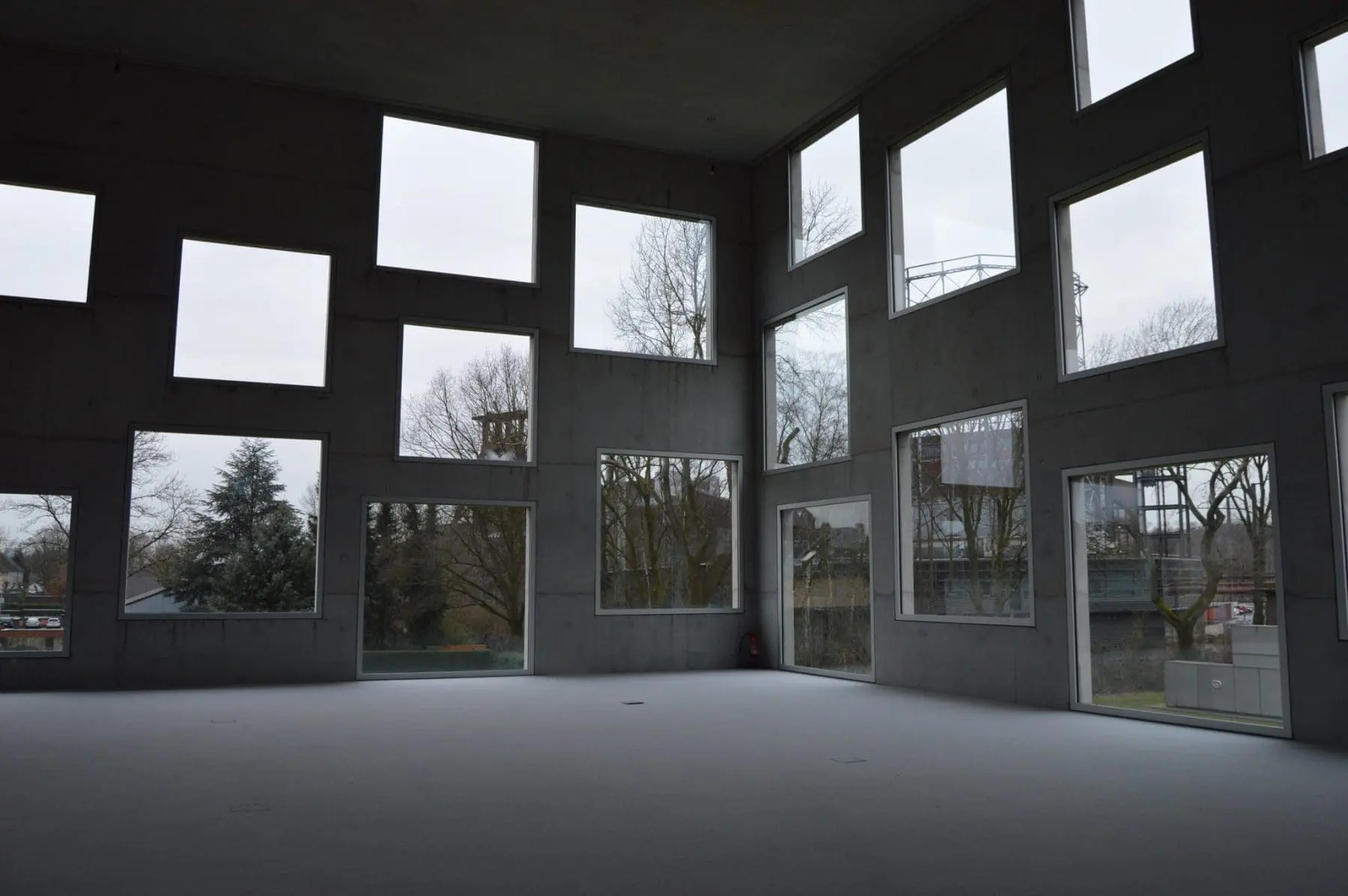

These fenestrations serve well to create an ambience with variety of light and shadow inside as well as serve an impactful elevation to the façade. The decision for the design and selection of the windows is not based on the only aspect of they providing light or they creating ambience, it is also based on how well they respond to the surroundings as well as how efficient they are to the environment around.
Types of Fenestrations
There are plenty of styles and designs to choose from for windows and openings. Here are some of the most impactful styles for windows along with their uses. These play an important role in forming the base for the openings along with providing a large scope for custom design development on every individual style.
1. Slit Windows
Function
These are one of the smallest openings or voids that serve as fenestrations. They provide intake of direct as well as diffused light and create a light and shadow pattern play in the interiors.
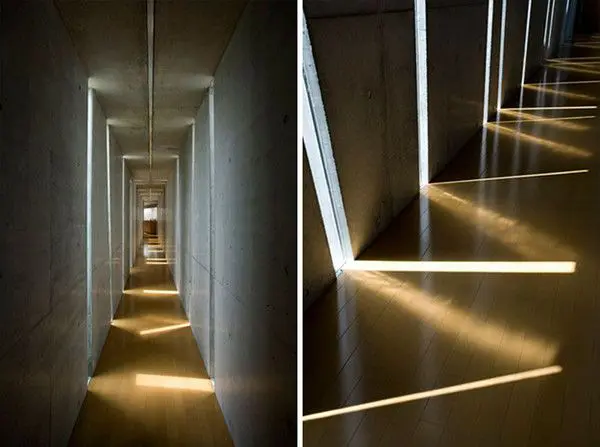

Usage
These are generally adopted to light up the passages, corridors and also along the façades of huge dead masses to break the monotony and create the necessary play of voids.
2. Jalis or Perforated Windows
Function
These are similar to slits but a patterned pre-casted or metal jail is present which have larger voids and variety of pattern designs can be achieved. They serve as a transparent façade yet creating the required bifurcation between two spaces or with the external environment.
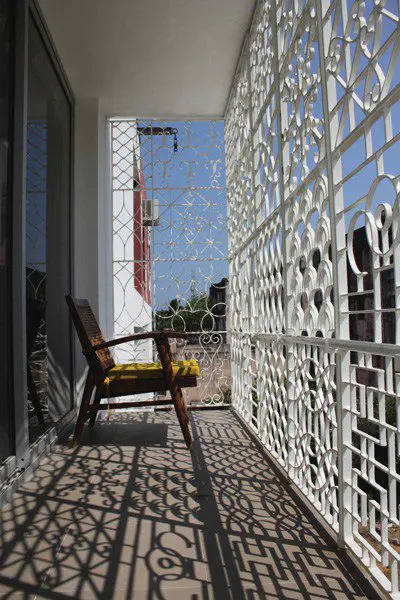

Usage
These are used along the balconies to create variety of ambience throughout the day along with the changing sun. They can also be used to cover huge solid voids and also as partitions in the interior spaces. The transparency between spaces can be achieved by sizing the voids accordingly.
3. Glazed Openable Windows
Function
These are the simplest and most efficient type of windows which can be designed in various shapes along with a variety of custom designed chajjas as these require weather protection due to larger voids. These are glazed and fixed with a variety of framing like wooden and metal.

Usage
Used majorly in all residential and also many commercial buildings. Used in bungalows and small scale apartment houses accompanied with curtains in the interior and designed chajjas and cladding alongside on the exterior façade of the window to highlight its beauty.
4. french windows
Function
These are generally through and through windows from floor to floor level with entire glazing supported with wooden or metal frames. They provide almost 90% transparency with the outdoors and give the perfect lighting glare required to light up the entire space or a particular room.
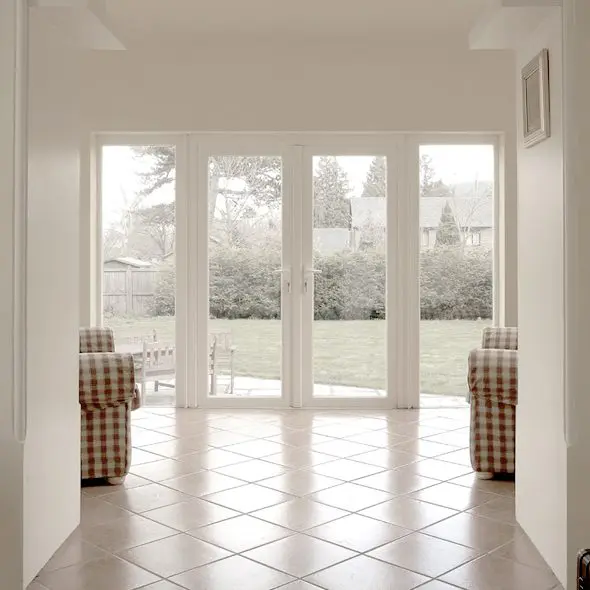

Usage
They are mainly used in bungalows with attached lawns or landscape giving an extended feel and view from the interior spaces connecting with the adjoining landscapes or the exteriors.
5. Folding Windows
1. Function
These are the best type of fenestration where it has to serve as a dual purpose – a partition as well as an open window. They fold along the tracks in horizontal as well as vertical manner.
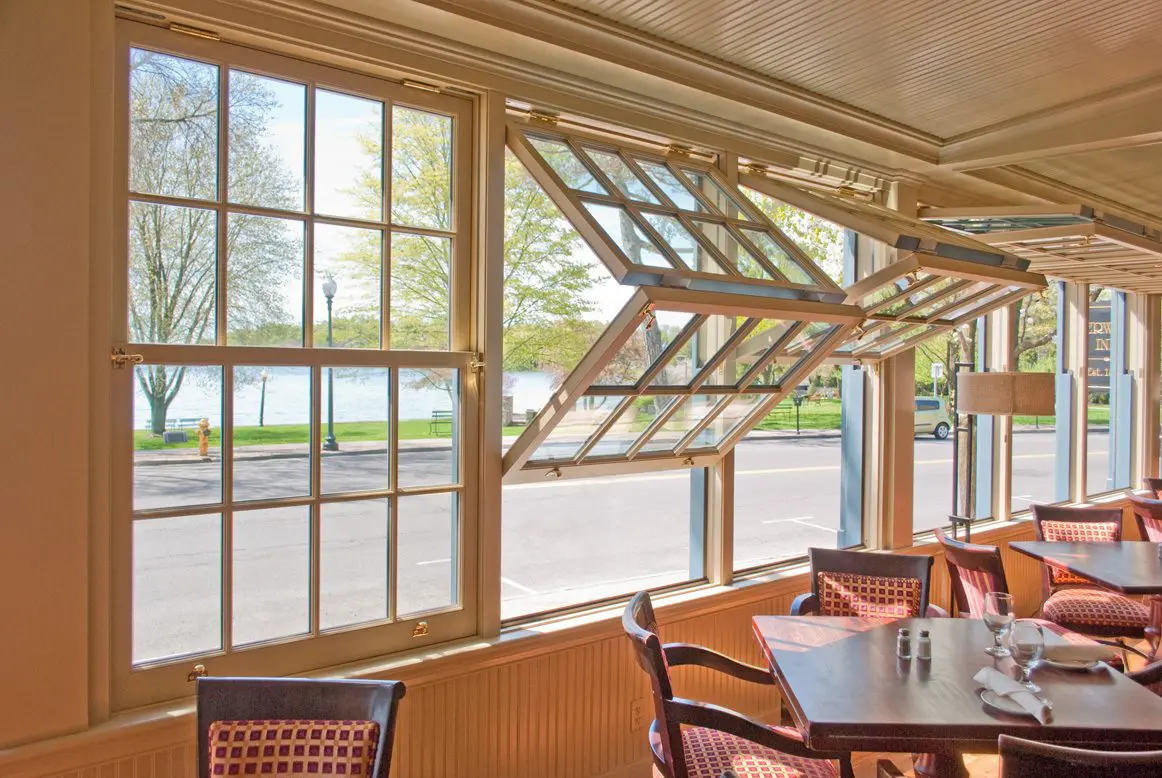

Usage
The highlighting feature makes it most suitable for open kitchens as well as for interior allied spaces. As per the requirement it can be folded and even partial transparency can be achieved through these. They can also be used for small cafes and kiosks where the counter needs to be opened or closed as per the timing requirements.
Types of Glazing
There are a lot many options for covering the voids formed for or by various fenestrations. The most commonly used method is glazing. Glazing is used as it mainly provides permeability for the light to enter and is also covered with a Protective Skin. The glazing used are mainly based on the impact of it on the environment. They maintain the thermal comfort along with the heat gain on site or inside the structure.
1. Double Glazed Windows
Double glazed glass is two glass sealed around the edges with an air space between the two to form a single unit. The insulating air / gas between the two layers of glass improve the thermal performance along with reducing the heat gain or the heat entering through the glass inside the structure.
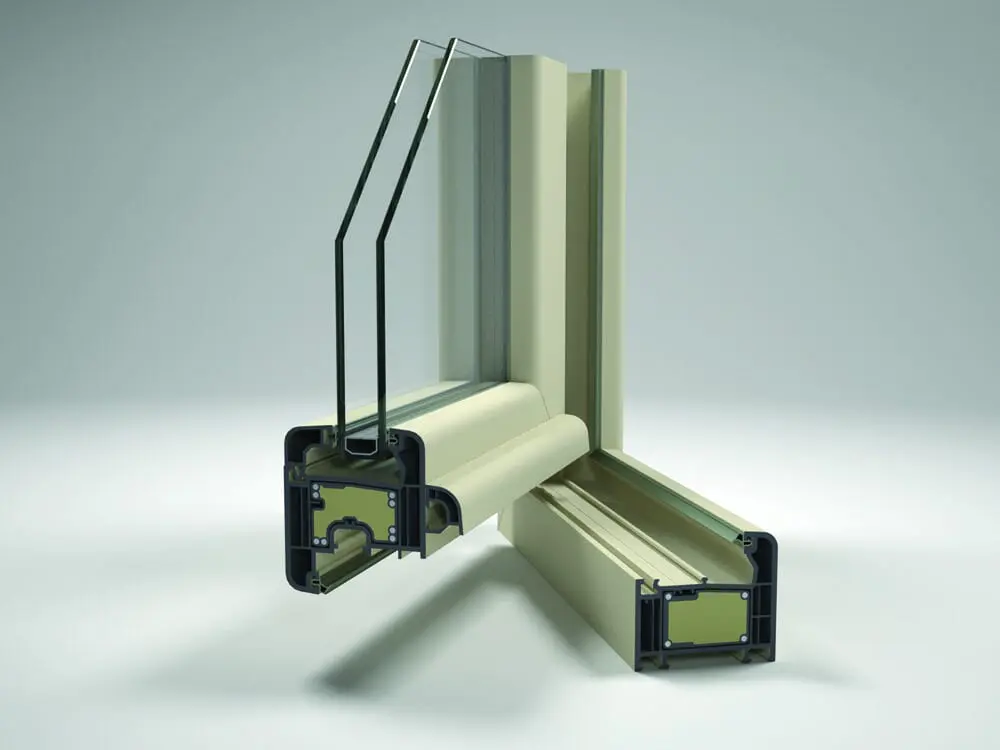

These are generally used in green rated or energy efficient buildings. They can also be used where there is direct contact of sun that is along the southern façade to reflect back the harsh light.
2. Triple Glazed Glass Windows
Triple glazed glass is three glass sealed around the edges with an air space between the two to form a single unit. The insulating air / gas between the three layers of glass improve the thermal performance along with protection against very harsh sunlight.

These are a step ahead then the double glazed glass with a more surplus due to the triple layering of the glass. Here the glass thickness can be reduced and these are more effective when there is seamless exposure to the sun and its harsh light.
3. Low E-glass
Low-e glass has a microscopically thin, transparent coating—it is much thinner than a human hair—that reflects long-wave infrared energy (or heat). Some low – e”s also reflect significant amounts of short-wave solar infrared energy to protect the interior spaces from the harmful rays.
There is mainly a thin coating which helps to reflect the particles and various wavelengths. This Low – e glass can be used double or triple glazed as per the requirement according to the surrounding climatic conditions.
This technique is the most effective for glazed buildings to maintain the thermal comfort as well as for huge glass curtain walls.
need and Role of fenestrations
Thus, fenestrations play an important role in maintaining the solid void ratio of the building along with making the building porous enough to breathe and reduce its carbon footprint on the surrounding environment. In this way fenestrations serve as a boon for light, ventilation and also scenic panoramic views from the structure along with creating an impact on the end user viewing it through the exterior or just passing by.
– Kushal Mehta