Green Building is about making the optimum use of resources throughout the timeline of building construction, with energy-efficient actions and designs. With numerous benefits from certifications to economic considerations, technology today encourages people to use more eco-friendly materials and local construction techniques with better performance and durability. Selecting the appropriate materials according to the geographical and cultural context plays a crucial role.
Some criteria to probe include longevity, compatibility and performance of the material concerning the entire building, contribution to reducing energy and water consumption, or improving air quality and waste management.

Organizations that provide provisions and distribute ratings in India include; Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA), Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), and Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE). Here are some eco-building materials, which are revolutionizing the construction industry.
1. Earthen Structures
Adobe, rammed-earth and other similar structures are perhaps the greenest material available in India and a great replacement to the traditional concrete masonry. It is composed of clay, dirt, gravel and lime. Harvested locally, they offer durability and insulation to buildings. Rammed earth can be used for walls and flooring and can act as thermal storage. It also recycles waste materials from quarries and has a low carbon footprint.

2. Straw Bale
Though rare in construction, straw bale has gained immense popularity in recent years. It makes use of agricultural waste and a good substitute for lumber. It also offers excellent insulation and sound deadening properties. It is resistant to fire and can match any aesthetic. Strawbale homes have thicker walls and therefore suggested when the area is in plenty.

3. Bamboo
Bamboo is a versatile material of high cultural, economic and social significance. It is light-weight, flexible and much cheaper than steel (tensile and compressive material). Bamboo can be used for ceilings, flooring, walls, partitions and structural components like beams and trusses in a building. It is easy to assemble and is abundantly available all over India. Engineered bamboo products are used for making medium to high-rise buildings. Mistaken for just a traditional material, it’s modern counterpart is still a relatively untapped market in India.

4. Natural Fibres and Cellulose Insulation
Insulation indicates how resistant a building is to losing energy. The insulation is made from recycled natural fibres to fit into any cavity. They are renewable resources and are available in certain locations. Similarly, cellulose is a common insulation material made from recycled paper. It is a green alternative to and is relatively inexpensive to fibreglass.

5. Engineered Wood
Two types of wood are well-liked by green builders – engineered wood and wood certified by various authorities. Engineered wood uses wood scraps and small trees to produce framing stronger than natural logs. It helps the builder use less wood per structure. There are many different treatments and techniques of construction available like acetylation, cordwood placement, etc which are both green and aesthetic.

6. Slate & Stone
Stone construction is an excellent green choice, but not fruitful on the economic side, due to high labour and material costs. The prices are relative to the availability of them. Stone is known for its durability, these structures last for decades. The use of slate is common in roofing systems, where it is available in abundance.

7. Plastic and Vinyl Composites
Materials like plastic and vinyl are recycled and combined with other materials to create various composites. These have a long lifetime and low maintenance requirements. Today materials like bioplastics and biocomposites and other plant-based building materials are on the rise. This practice also helps in reducing trash and aids in recycling.
Mycelium, a futuristic material made from the roots of mushrooms is used for making bricks and other lightweight objects.

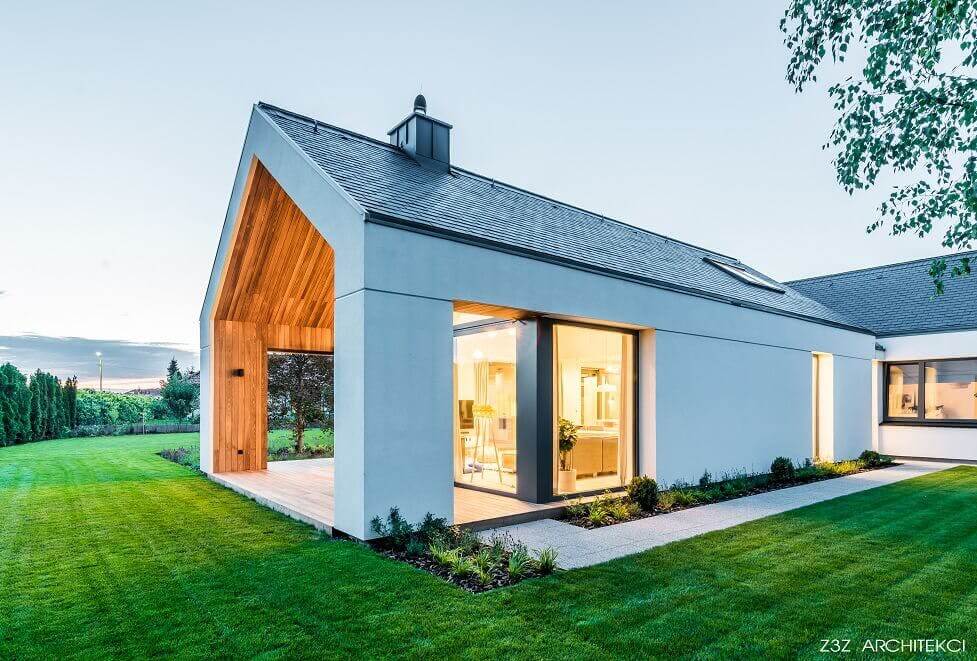
8. Grasscrete, Hempcrete and Ashcrete
A method of laying concrete with spaces for grass to grow, grasscrete reduces overall concrete usage and improves stormwater absorption and drainage. Hempcrete is a material made of woody fibres of the hemp plant with concrete.

9. Structural Insulated Panels (SIP's)
These are large panels typically made in factories. The panels consist of foam insulation sandwiched between two sheets of OSB( oriented strand cardboard). They have extraordinary air sealing and insulation properties. Some drawbacks include an expensive installation process and low fire resistance.

10. Natural Clay Plaster
A green alternative to common gypsum plasters, when paired with good workmanship, can provide a beautiful earthy finish to interiors. It is non-toxic, biodegradable and dust-resistant. It absorbs moisture, keeping humidity at bay and regulating room temperature.

11. Low Volatile Organic Compound paints, stains and coatings
Paints are a common source of indoor air quality issues and the formation of ozone due to the emission of harmful VOCs. These VOCs propel quick evaporation of liquids in paint, leaving an unsightly solid film of colour.

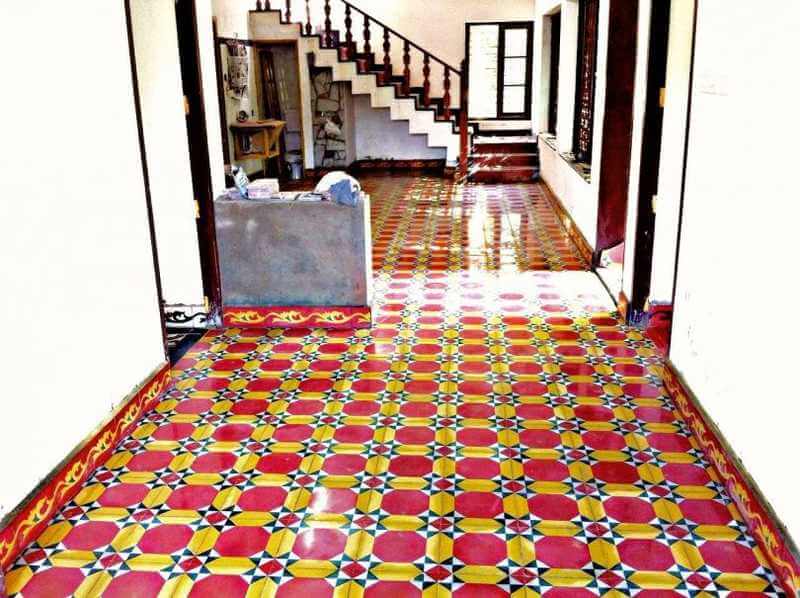
12. Organic Tiles
Excess mining is a growing environmental issue in India. Some examples include Athangudi tiles, terracotta tiles, kuddahpah and yellow sandstone. They have attractive colours and finishes. These can also give any space an ‘Indian Vintage’ look.

– Asmita Kothari