Most people are familiar with the term ‘net-zero building’. You hear about how much people love such a building and how relaxing it is to live in one. Not to mention the energy costs they save while helping the environment. With the rise in global warming and resource exhaustion, these buildings have been proven to be a key in a path to a greener future.
However, we simply can’t make a building net-zero just by knowing its name. There are a lot of processes involved that require attention from the architects and designers.

What is Net-Zero?
A net-zero home is build using energy conservation methods and uses materials that aren’t a drain on natural resources. While there are many eco-friendly homes around, net-zero homes are several steps ahead of those homes.
Not only do they conserve energy, but they also create it. Net-zero homes are built to be air-tight with insulation so that they produce as much renewable energy as they conserve.

What is the Difference Between Net-Zero Homes and Green Homes?
A lot of people believe that net-zero is just another term for green. Although both focus on energy conservation and are environment friendly, there are, however, a few critical differences between green homes and net-zero homes. A green home is an already existing property that has been upgraded to a state of higher energy efficiency.
Meanwhile, a net-zero home is almost always a newly built structure. Additionally, green homes follow most of the same ideas and building planning as net-zero homes, they don’t adhere to the same strict standards as zero-energy homes.

One crucial difference is that the percentages of energy saved in a green home are usually around 60 to 80%. These numbers may seem impressive compared to standard homes, but the percentages pale in comparison compared to the 100% saved energy in net-zero homes.
What are the Affordable Ways to Make Your Home Net-Zero?
The cost of any home, including a net-zero home, depends on various factors, such as location, building type, design features, building materials, additions, and appliances. When it comes to net-zero homes, people always believe that they cannot be built affordably. This is due to the lack of knowledge provided to the general public.
However, in recent years, designers and builders have found many innovative ways to save money while building net-zero homes. On average, the difference in construction cost between standard and zero-energy homes is approx 500 Indian rupees per square feet. Also, the average size of an Indian house is 494 square foot.
So, in general, the additional costs for making your home net-zero is even less than 2.5 lakhs. This extra cost can make your home carbon-free, eco-friendly, and a lot better than standard homes. So, it is worth the effort and money. Below are a few affordable ways to make your home net zero.

a. Smart design
Smart design is the core of a zero-energy home. The number of energy-efficient materials and construction practices need to be integrated into the early phases of designs.
For a successful net-zero home, architects and designers work closely with their builders and recognize the necessary steps and strategies involved in constructing zero-energy homes.
b. Site selection
The first step would be site selection. Usually, the ideal site for a net-zero home should have unobstructed sun, flat topography, and little exposure to the weather. Another site requirement is that it should be located near access to services, shopping, and mass transit.
c. Building Orientation
The building orientation is a process that should be done in such a way that it would take the greatest advantage of seasonal sun angles for both passive heating and cooling. For solar panels, the ideal orientation would be the southern roof orientation.

d. Climatic Considerations
Climate should be a major consideration while designing zero-energy homes. The insulation levels, air tightness, moisture control strategies, daylighting, and other design elements need to reflect the local conditions. Moreover, you have to pay special attention to the design in hot climates.
e. Simpler Shapes
Consider using fewer and simpler shapes rather than complex shapes. Less architectural complexity will be easier and cheaper to build, air seal, and insulate in the field. Also, try to use only one type of ceiling throughout the house.
Flat or cathedral ceilings are preferable for net-zero homes. The variation in ceiling types would change the heights and then create a high wall that can be tricky to air seal and insulate.

f. Air Tightness and Mechanical Ventilation
The air tightness standard should be specified after the completion of the plans. This is usually expressed in air changes per hour at 50 Pascals (ACH50). The threshold required to reach net-zero energy should be 2.0 ACH50 or less. Mechanical ventilation equipment and ductwork must be added to the design plans. They should be located within the conditioned envelope of the building.
g. Energy modelling
Energy modeling is important to determine which energy-saving features are most cost-effective. Designers identify the cheapest measures required to create net-zero homes with the help of energy modeling software. An energy modeler provides clients with energy solutions, strategies, options, and technologies to meet their energy efficiency objectives.
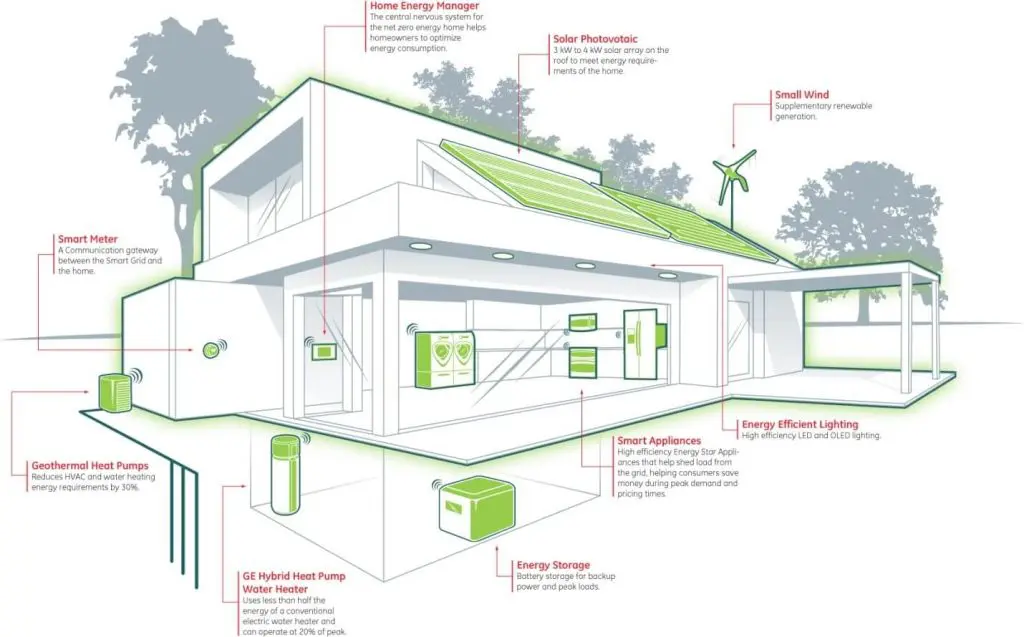
h. Insulated Windows and Doors
Insulated window glazing refers to windows with more than one pane of glass. The glass panes are spaced apart and hermetically sealed, leaving an insulating air space. However, that’s not all there is to it when it comes to insulated windows and doors. The fact that more heat flows through the frame than the insulated glass unit is often overlooked.
So, look for windows or doors that have the smallest frame profile. It is also more energy-efficient to use fewer, larger windows and doors with the same glazing area because larger fenestrations have a higher glass to frame ratio.

i. Energy efficient lighting
Reducing the energy required for heating and cooling is a necessary step to meet the net-zero goals. You need to use air-source heat pumps as it is the most energy-efficient heating and cooling system currently available.
It takes heat out of the air and moves it as hot refrigerant through a small pipe into one or more indoor units that deliver heat into the house. In warm climates, high SEER mini-splits are much more energy-efficient than standard air conditioners and they are especially suitable for warmer climates.

g. Solar Panels
Well-place solar photovoltaic (PV) panels are one of the most cost-effective renewable sources of energy for net-zero homes. They can power everything, from lighting and heating appliances, and even cooling systems. A net-zero home has a lot of windows that make full use of the use and it will significantly lower a home’s energy needs for indoor heat and lighting.
Ideally, the PV panels should be placed somewhere with unobstructed sunlight. The south side is the best option as it has the most sunlight between 9 am to 4 pm. The estimate of the annual energy use of the home can be measured through energy modeling.
Once you do that, you can ask a solar contractor to calculate the size and cost of a PV system capable of generating that amount of energy over the course of a year. A solar contractor will also tell you how much roof area would be required for installing the panels.

h. Sealing the Building Envelope
Air sealing is another cost-effective method to reduce space heating and cooling energy use. It also improves indoor air quality significantly. Achieving such a high level of air tightness requires lots of steps and details. You need to identify the thermal boundary and then ensure that there is a continuous air barrier along the entire boundary.
For continuous air barrier, identify the exterior structural sheathing or the interior drywall, and then bridge the gaps or joints between them to completely seal the boundary. The cost of such advanced air sealing methods varies depending on the materials and labor cost.

i. Insulating the Building Envelope
As mentioned above, insulating the doors and windows is an important element for net-zero homes. However, it is quite common to overlook the fact that heat is transferred through walls, floors, ceilings, and pretty much every single element in the house. Insulating all the sides of the building envelope is a fundamental step for achieving the zero energy goals.
To insulate the building, you need to use high-performance walls and advanced framing techniques. The majority of building materials resist the flow of heat to some degree and this thermal resistance property is defined as R-value. Every material has different a R-value. While selecting the building materials, make sure to use those with high R-vales.
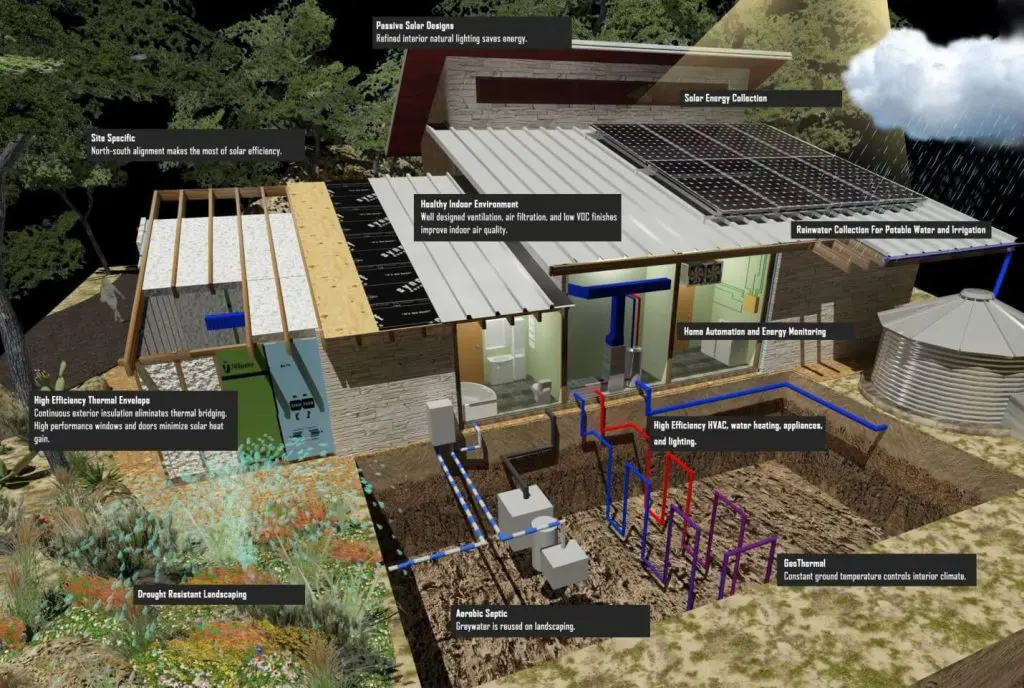
A net-zero home at a low price is an achievable goal if you start the planning early on. Though the initial costs would be higher than your standard homes, it is a one-time investment that will prove its worth over time.
– Tulisha Srivastava