Electricity was an ever important discovery for mankind. Be it basic necessities to exquisite designs – electricity has a major role to play in every sphere of our lives. Several technological advancements in the type of appliances have come to the fore, and this keeps on increasing day after day.

Electricity was born to serve man, its master. But with the current scenario of several mishaps and lack of preventions, there has been a strange and undesirable role reversal.
The human body has chances of severe damage in case an electric current of 5 milli Amps passes through it within a rapid time span.
In such a case if a person touches an appliance, which has heavy currents flowing through it, with his bare hands there are high chances of this encounter being fatal.
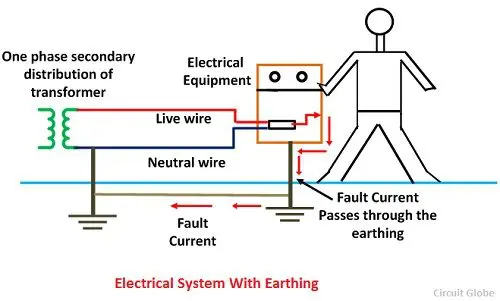
The electrical potential of the Earth is considered to be zero. Hence on connecting the electrical channels of any appliance to the Earth, its potential would become zero too.
This is the main concept behind Earthing, which is a process bonding noncurrent bearing parts of an electrical device or the neutral summit of the electrical organization to the earth through wires possessing minor resistance to flow of current.
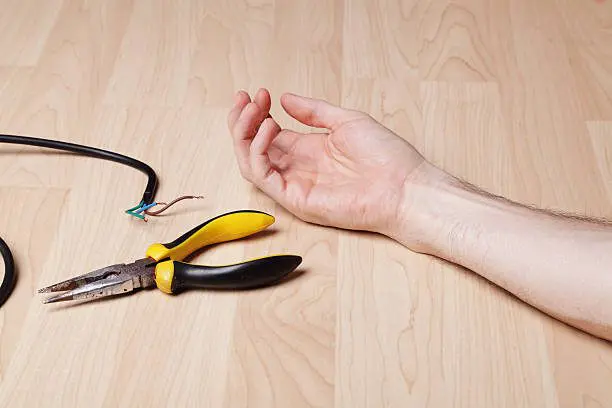

Why is Earthing required for Houses?
- To warrant that all pieces of equipment in use by the occupants of a building are at Earth Potential, thus safeguarding them from electric shocks through direct contact
- To protect electrical apparatus from getting damaged due to weighty currents along electrical lines
- To sustain stable voltages in three phase circuits even under unstable load state
- To protect tall buildings from getting harmed under lightning
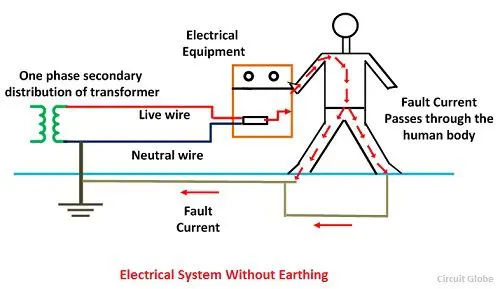
What Happens if an appliance is Earthed Properly
We know that current flows from a higher to a lower potential. Any electrical appliance or any electricity line which has been connected to the earth is now at zero voltage.
In the case of any overloading of current, the immediate discharge of electrical energy takes place to the ground, without harming the appliance or the user.
Even if the insulation of the equipment fails, if it is earthed, the appliance is safe enough.
Types of Earthing
Broadly speaking, the earthing of electrical equipments and lines are classified into two types: System Earthing and Equipment Earthing.
1. System Earthing
This is the type of earthing which is associated with current carrying conductors. It is quite relevant because there might be overflows of currents during the process of its transmission. This type of earthing is put to use in stations and substations of electrical supply.

2. Equipment Earthing
This is the prime type of earthing for homes and other buildings. It deals with the safeguarding of noncurrent carrying apparatus and metallic conductors. This type of earthing serves the dual function of protecting the user of the appliance against shocks, while at the same time safeguarding the appliance from getting harmed.

methods of Earthing
There are several common methods employed for earthing of appliances, and each of them is used according to the site of the building, the type and number of appliances to be earthed, the budget and other such factors. Here are a few of them.
1. Plate Earthing
A 2.5 metre deep pit is dug into the ground and a Galvanised Iron (GI) plate is placed inside along with charcoal and sand for the purpose of maintain low resistance around the plate.
An earth wire, which is of GI or tinned copper, is bolted to the plate before burying it by means of nuts, bolts and washers.
The wire is made to pass through a GI pipe through which some water is poured in to increase conductivity. The earth wire is connected to the Earth point of the socket and is finally covered.
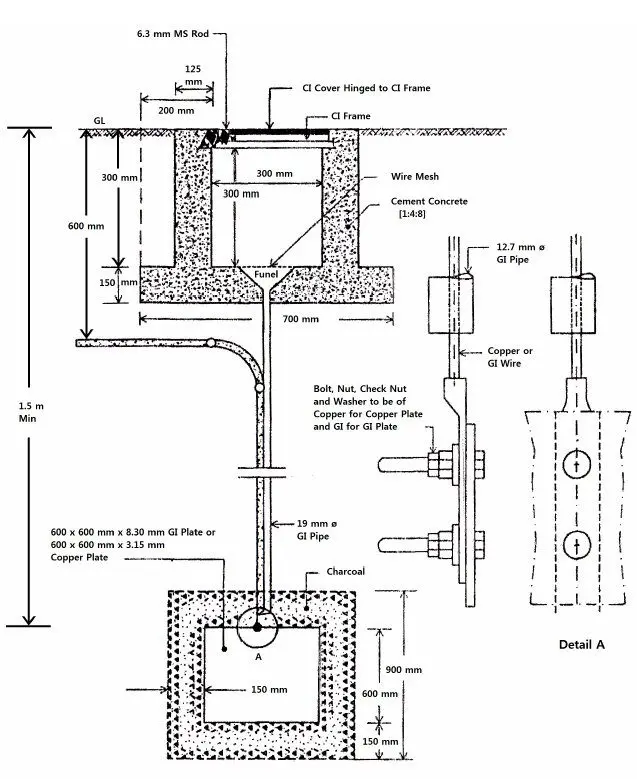
2. pipe Earthing
A 2.5 metre long pipe measuring about 35-75 mm in diameter is buried in the dig out pit along with sand and charcoal. The pipe is provided with several perforations to maintain dampness around and hence conductivity.
The earth wire is tied and clamped near the summit. Water may be poured into it during summers. The earth wire is safer against damage in such a setup.
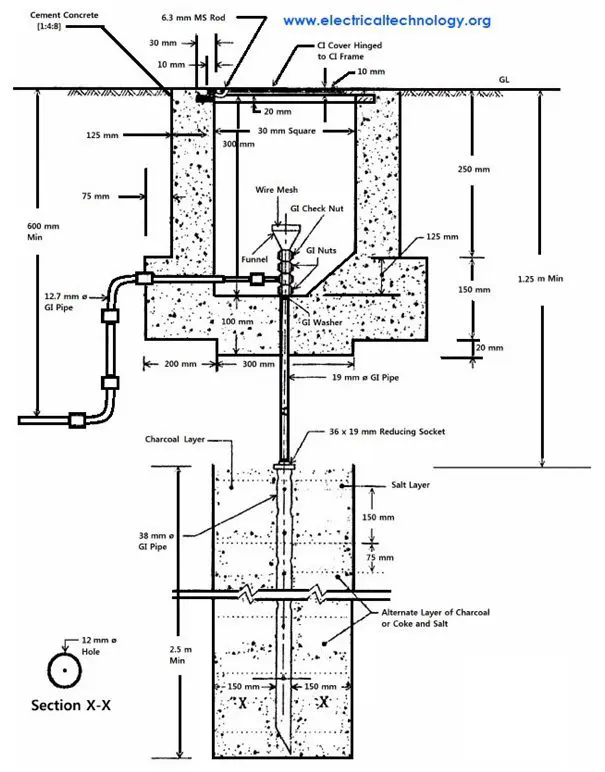
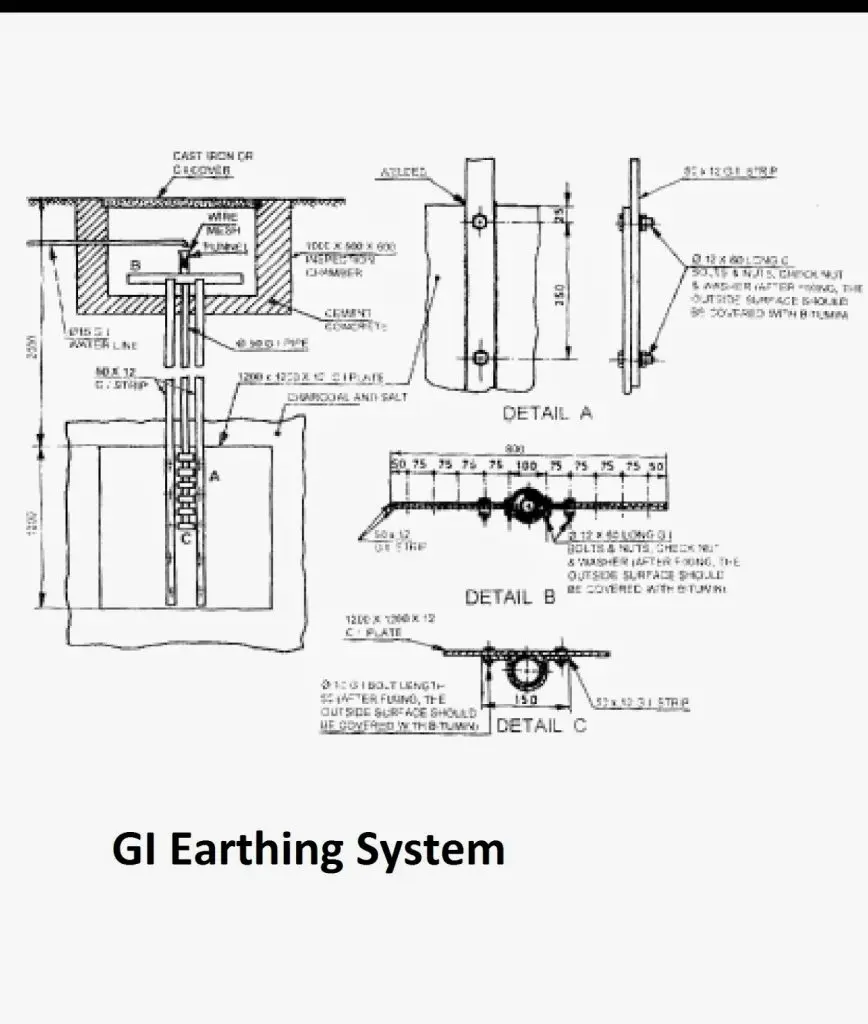
3. Rod earthing
This method employs hammering of zinc and copper rods of about 1-1.5 metres length and 12-20 mm diameter into the general mass of the earth.
Successive rods are screwed together and this chain is tried making as long as possible for lowered resistance by the surrounding soil.
The earth wire is tied and clamped near the summit. This is a very economical and quick procedure for earthing.

4. Earthing through a Water Pipe
We know that hand pumps are used to extract water from the water bed, which lies well inside the ground. To the GI pipe of a hand pump, the earth wire is tied and clamped.
This pipe serves as an excellent electrode for carrying excessive currents deep below the ground.
However, the difficulty lies in the probable shocks to users of hand pumps if the earth wire is not clamped tight enough.
– Sourav Suman