Wonder how you can minimize those losses on energy? Ever wished your pockets wouldn’t have to be emptied every month over large electricity bills? Do you want to know if it is possible to conserve energy in your own little ways for your dream house?
If yes, we bet you give this article a read. An insight into low energy and even zero-energy houses, and tips to save those extra bucks is what this write-up talks about.
A Zero Energy Home
Yes, you get that right. A Zero Energy Home is a home which, on an average, uses practically no net introduced energy over a span of time, generally taken as a year. Speaking in calculative terms, a Zero Energy Home wouldn’t use more energy than generated by it, in the course of a year. Some homes might even be monitored to produce some amount of surplus energy, with proper conservation and energy generation (microgeneration) techniques. We shall focus only on Zero Energy Homes in this article.
Architects today have started focussing more and more on such techniques of low-energy consumption, based on the three E’s – Energy, Economy and Ecology. The concept of Passive Solar Design can add up a lot to achieve the goal of minimalistic energy consumption. Not like it’s a thing of today: the first zero energy building (ZEB) was built way back in 1979. Even you, with the application of a few techniques, can transform your home into a ZEB.
How to Construct a Zero Energy Home?
1. Designing Your House
A few considerations while designing your house could have a great deal of impact on lowering the imported energy consumption of your home, thus bringing it closer to the zero energy goals.
Your building should be designed to capture the morning sun, be it through a clever orientation, or proper utilisation of windows. The building’s longer side should have an east-west axis.
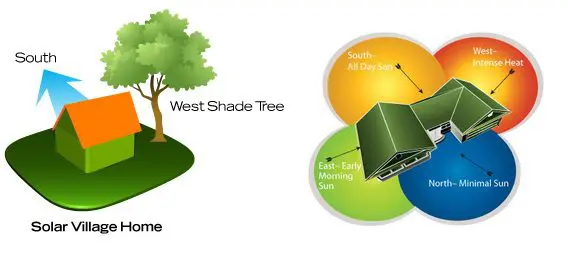
The design of windows and their overhangs should be such that they provide adequate sunlight in winters, and keep the sun at bay during summers.
You could go innovative in the type of shades and shutters for your windows. Try to keep natural by using shrubbery, trees, trellises or go high on interiors by using decorative blinds and curtains; your choice!
Judicious and clever use of insulation, radiant barriers and thermal mass are a go-to option. After all, passive solar designing depends on thermal storage and transfer.
2. going Solar
A preferred alternative for passive energy design, solar access plays a crucial part in a number of ways. Number one, it allows natural light and heat into your space. Solar panels, solar cells, solar water heaters are paving the way for a literal ‘solar wave’.
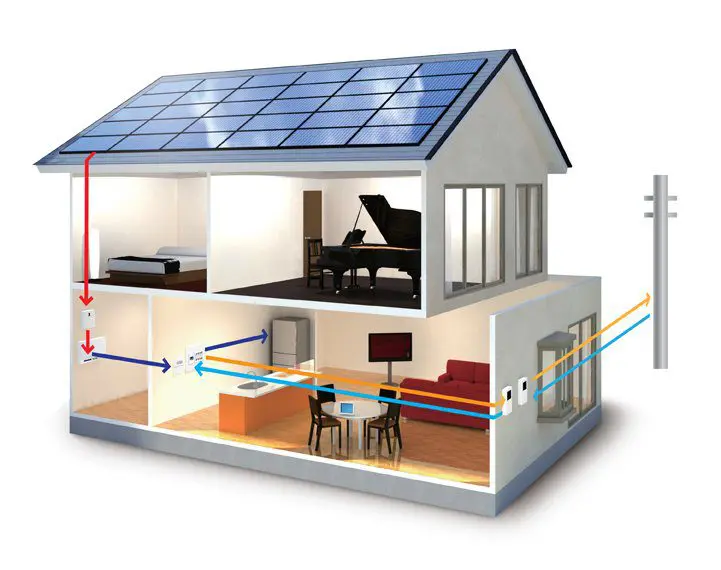
A clever way to get rid of those electricity-driven heaters and geysers, and all those long bills for keeping lights switched on during the day. The solar orientation of the building, the sun path in the area for different hours and different seasons and details required for the installation of the solar devices are a few must-knows for this purpose. An extensive site analysis and calculative techniques are the keys to achieving a zero-energy design by implementing passive solar designing.
3. Efficient Lighting
One of the primary attempts at minimizing the energy consumption in a building would be planning a judicious lighting system. This could be achieved with a blend of passive solar lighting and sustainable light designs, and few moderations in interior designing. With the proper placement, selection and sizing of windows, the amount of daylight as well as excessive thermal loss can be regulated. One important thing to keep in mind is proper heat regulation.

For the night times, dimly lit interiors or for cloudy days and twilights, when natural daylight is either not adequate or unavailable, the creative and clever use of sustainable lighting can really up the game.
CFLs (Compact Fluorescent Lamps) and LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are no more alien terms to us. Add to them more technologies like PLEDs, organic LEDs, and other low voltage lighting substitutes, and you get an array of low-energy options that can brighten up your world, literally.
4. Materials
A correct choice of materials certainly affects the energy efficiency of buildings. Several sustainable materials are being put to use for the construction of building exteriors, interiors, wall paints and thermal mass.

Green facades and interior landscaping are interesting ways to improve your building’s energy efficiency, at the same time lending aesthetical value like no other. Compressed Earth Blocks, Flyash Bricks, wood, bamboo, Recycled Glass and Plastics, and other natural and organic materials, there are numerous options to choose from!
5. Automation Techniques
Home automation is what we’ve being been doing for ages – saving electricity by little measures such as switching off appliances when not in use. Not much goes in remembering to switch off that fan or light when you leave the room. Not much goes in understanding and optimizing usage of appliances such as televisions and computers for the purpose of energy saving. Besides, we have several devices to improvise home automation techniques.

Smart power strips that control power consumption and smart thermostats that stop cooling or heating if they detect abandonment of space, are new feats in engineering technology. Certain security systems and remote controls in tablets and smart phones have been so designed as to look after lighting, HVAC and appliance overuse.
6. Green Roof
A green roof is exactly what you think – a roof, either wholly or partly, covered with vegetation atop a waterproof sheath. A green roof has more benefits than you can imagine. Apart from providing heat insulation and helping in energy conservation, it helps in the absorption of rainwater, improving the mental health of the inhabitants and neighbours, lowering the surrounding temperatures, and providing a welcome zone for birds and butterflies and other things pretty!

7. Landscaping gardens
The proper use of landscape elements can assist greatly in controlling heating and ventilation of your home, resulting in lesser bills and greater savings.

Vines, hedges, pergolas, vertical gardens, trellises are all few of the many options to choose from. You could use landscaping for shading and also to maintain healthy surroundings. The energy efficiency comes from a smart combination of hardscape materials and softscape plants. Organic Gardening and Composting practices are sustainable practices of gardening.
So here we go with a few suggestions for switching your home into its energy efficiency mode. And there are many more! Hope we helped you with this little attempt towards ZERO ENERGY BUILDING design.
– Sakshi Singh