Any home in a subtropical and warm climate of India needs to have a good ventilation system for proper air circulation within its rooms thus preventing it from being stuffy for its dwellers. Ventilation could be natural or artificial.
By natural ventilation we refer to a system that puts to use the equipments and designs to implement natural forces so that there is a supply of fresh air and heat dissipation for a comfortable living. It is distinct from artificial ventilation in that it doesn’t require mechanically driven (fan forced) ventilation and relies on winds and their properties such as buoyancy to deliver freshness to indoor and semi-outdoor spaces.

Types of Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation may be categorised as either Controlled or Uncontrolled.
Type#1. Controlled Ventilation
This is an intentional design for ventilation of a space with the help of suitable and strategic positioning of windows, doors, ventilators an d such relevant openings for proper wind circulation within a home. It is controllable by the dweller of the home too with the help of blinds, shutters, curtains and blockages.
Type#2. Uncontrolled Ventilation
It refers to the haphazard flow of air through unintended openings such as cracks and crevices within buildings. This is not designed and in some cases might even be objectionable. The only measure of controlling such ventilation is by corking in the gaps which cause such kind of ventilation.

Why Natural Ventilation is Required?
Air movement within our houses is as desirable as it gets. Apart from being source of supply of fresh air for breathing, ventilation helps bringing down the indoor temperatures through convective and physiological cooling, thus lending more comfortable indoor living conditions, especially in hot summer zones.
Supply of Fresh Air
The demand and usage of fresh air depends largely on the number of occupants of a house and the nature of their activities during different times of the day. Houses have to have permanent ventilators mandatorily and these cannot be shut off. Hence such ventilators are usually located on the upper part of walls, and have some kind of intricate working to reduce visibility and maintain privacy.
Windows must be provided in rooms preferably on more than one wall to achieve good cross ventilation an increase comfort. The size of window openings depends on the dimensions of the room and also on the orientation of the house. You wouldn’t want large windows on the South or West and let all the afternoon sun come in. The movement of air through cross ventilation acts as a heat carrying medium and thus lessens indoor temperatures to a great extent.
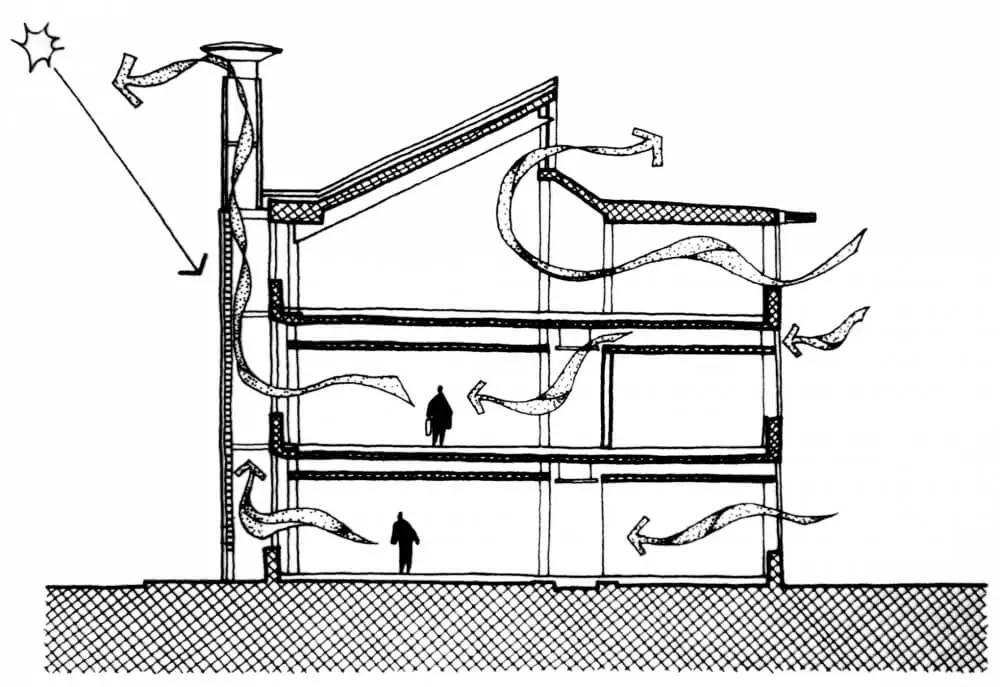
Why to Have Natural Ventilation?
The demand and usage of fresh air depends largely on the number of occupants of a house and the nature of their activities during different times of the day. Houses have to have permanent ventilators mandatorily and these cannot be shut off. Hence such ventilators are usually located on the upper part of walls, and have some kind of intricate working to reduce visibility and maintain privacy.
Windows must be provided in rooms preferably on more than one wall to achieve good cross ventilation an increase comfort. The size of window openings depends on the dimensions of the room and also on the orientation of the house. You wouldn’t want large windows on the South or West and let all the afternoon sun come in. The movement of air through cross ventilation acts as a heat carrying medium and thus lessens indoor temperatures to a great extent.
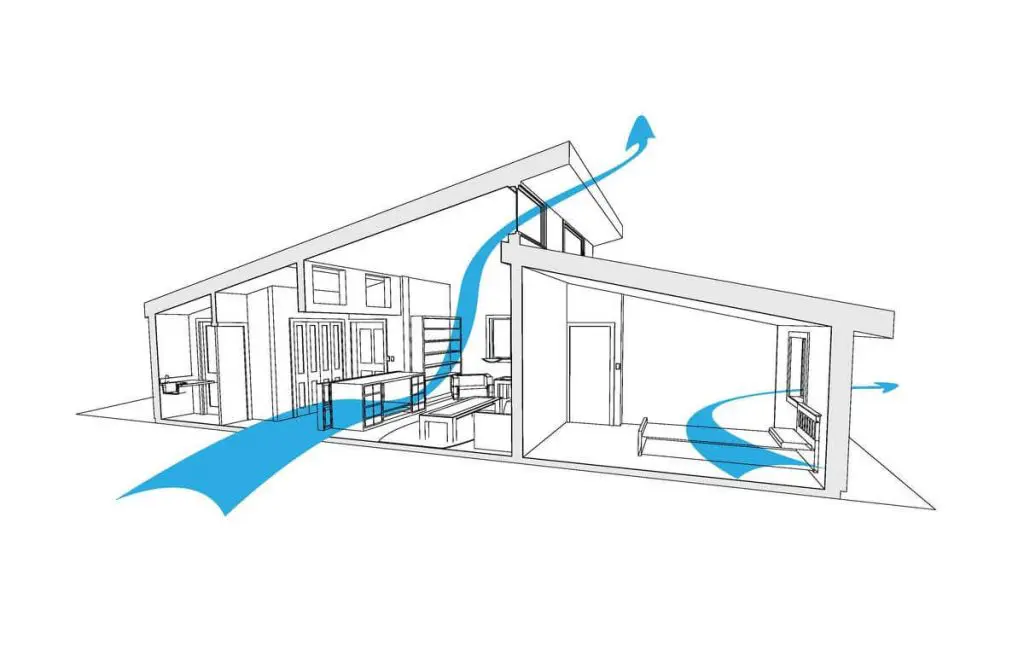
How effective is Natural Ventilation?
The demand and usage of fresh air depends largely on the number of occupants of a house and the nature of their activities during different times of the day. Houses have to have permanent ventilators mandatorily and these cannot be shut off. Hence such ventilators are usually located on the upper part of walls, and have some kind of intricate working to reduce visibility and maintain privacy.
Windows must be provided in rooms preferably on more than one wall to achieve good cross ventilation an increase comfort. The size of window openings depends on the dimensions of the room and also on the orientation of the house. You wouldn’t want large windows on the South or West and let all the afternoon sun come in. The movement of air through cross ventilation acts as a heat carrying medium and thus lessens indoor temperatures to a great extent.
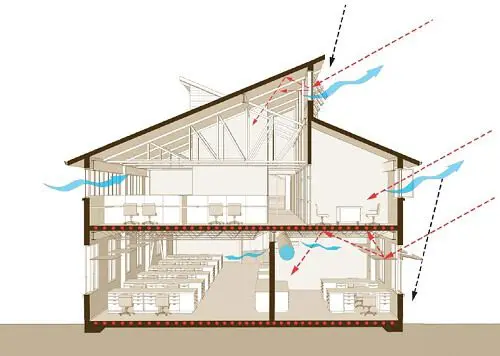
Principles involved in Designing of Natural Ventilation
The demand and usage of fresh air depends largely on the number of occupants of a house and the nature of their activities during different times of the day. Houses have to have permanent ventilators mandatorily and these cannot be shut off. Hence such ventilators are usually located on the upper part of walls, and have some kind of intricate working to reduce visibility and maintain privacy.
Windows must be provided in rooms preferably on more than one wall to achieve good cross ventilation an increase comfort. The size of window openings depends on the dimensions of the room and also on the orientation of the house. You wouldn’t want large windows on the South or West and let all the afternoon sun come in. The movement of air through cross ventilation acts as a heat carrying medium and thus lessens indoor temperatures to a great extent.
Single Sided Ventilation
With openings on only one side of an covered space, such as a room or a hall, single sided ventilations are quite popular, especially in apartments which share common walls and hence chalk out the provision of windows on any other walls.
The main driving force for the ventilation is the turbulence of the wind and air is bound to enter and leave form the same opening after bouncing back. This kind of ventilation is unsuitable for spaces which have large depth and ventilation is usually poor.
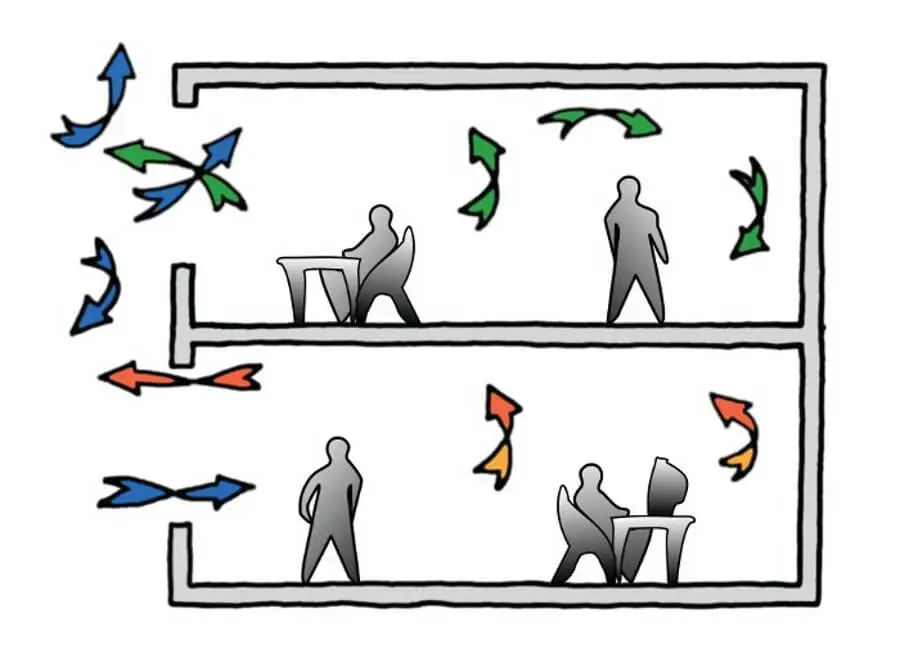
Cross Ventilation
In such a design there are opening on two opposite walls of an sheltered space. The air enters from one opening, and leaves from the other, channelling a clear pathway of air movement within the room.
The air also acts as a heat and dirt carrier as it moves. It provides excellent ventilation provided the outside ambience is good enough too. Suitable for deep plan spaces, it is one of the most effective forms of ventilation in use.
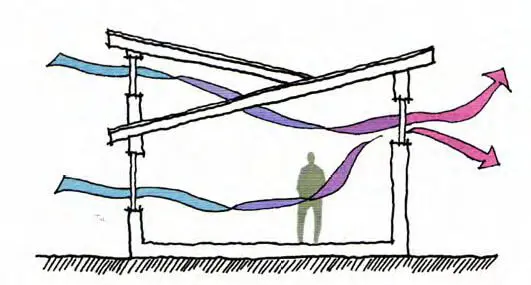
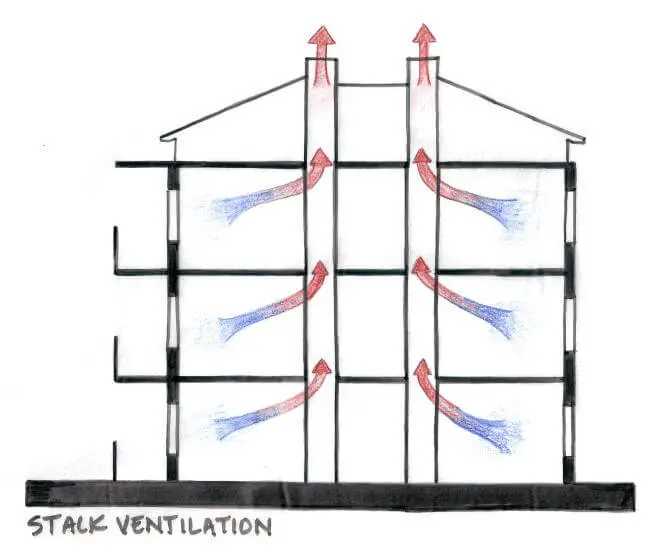
Stack Ventilation
In such a design there are opening on two opposite walls of an sheltered space. The air enters from one opening, and leaves from the other, channelling a clear pathway of air movement within the room. The air also acts as a heat and dirt carrier as it moves.
It provides excellent ventilation provided the outside ambience is good enough too. Suitable for deep plan spaces, it is one of the most effective forms of ventilation in use.
– Sourav Suman