Classification of Doors
Doors can be classified into many types based on the
- Working Operations
- Materials Used for Manufacture/fabrication
- Methods used for Manufacturing
- Components used
Types of Doors Based on Working Operations
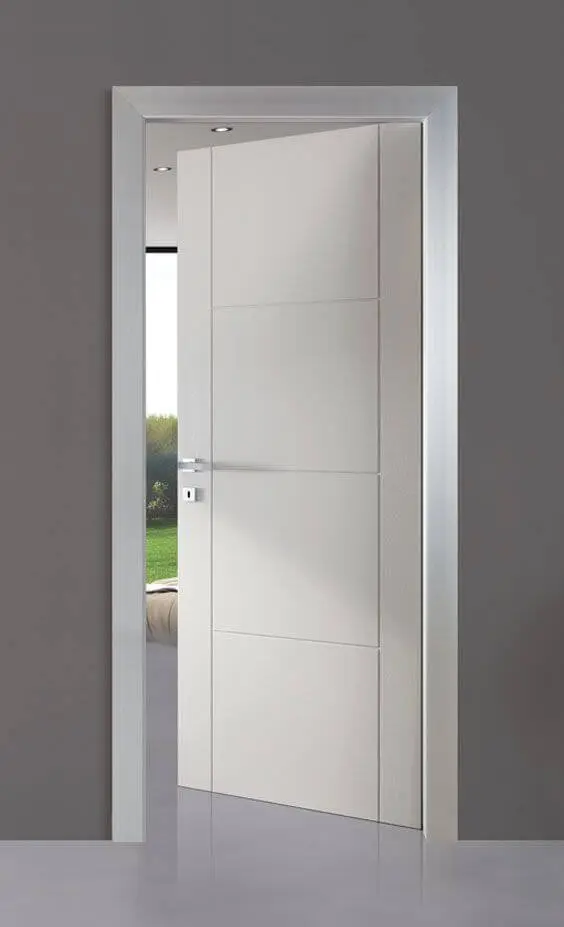
1. Hinged Doors:
The most common door type are Hinged doors. The door is fixed on one side to allow the door to pivot away from the doorway in one direction or the other. The Axis of rotation is vertical.
Advantage: The advantage is that the hinges used are inexpensive and requires minimum maintenance.
Disadvantage: This type of door take precious space to swing in/out.

2. Swing Doors:
Swing Doors are same as hinged doors, but here the Hinge can be rotated in either direction

The shutter is fixed to the frame with double action spring hinges which enables the movement on either side. A slight force will open the door, while the spring action in the hinge brings the shutter to close position. This return of shutter will be at a force, so the door has to be fully glazed or put a peep hole at eye level to prevent accidents.
3. Revolving Doors
A revolving door has a central shaft with four Wings that hang on it, The Shaft Rotates around the vertical axis within a round enclosure.
The central shaft is fitted with ball bearing arrangement at the bottom, which allows the shutters to move without any jerk and making noise.
The radiating shutters may be fully panelled, fully glazed or partly glazed.
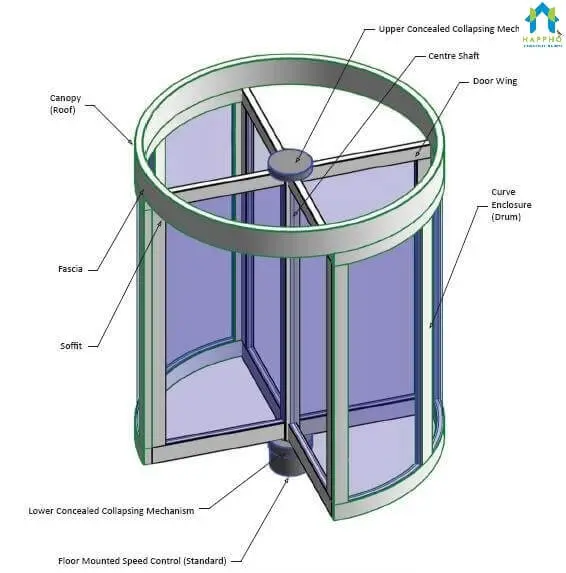
The doors (glass) generally allow people to see and anticipate each other while walking through.
Vertical rubber pieces are provided at the rubbing end of the shutter to prevent drought of air
4. Sliding Doors
These doors are generally used where there is place constraint for the swing of a Hinged door or for Aesthetic purposes. These doors are commonly used in commercial structures.
The shutter slides horizontally along the tracks with the help of runners and rails. The door is hung by two trolley hangers at the top of the door running in a concealed track, while at the bottom rollers are provided to slide the shutter in the channel/track. To ease movement plastic rollers are fixed at top/bottom.
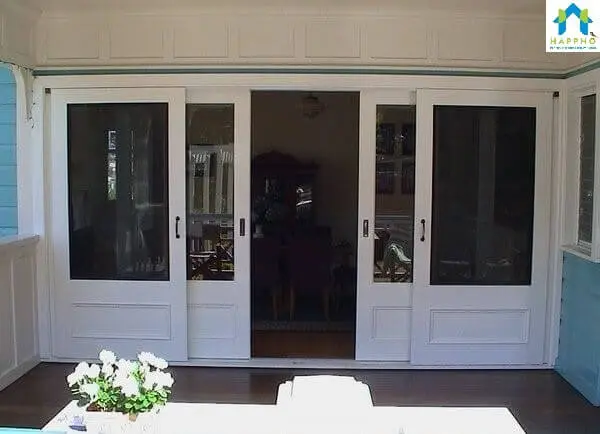

A sensor can also be attached at the top for the door to automatically open/close during movement of people.
Advantage: Can be Easily cleaned/Maintained, very good aesthetic feel.
Disadvantage: Sound insulation is pretty poor. The quality of materials used in doors and labor should be hi. Any faults in fixing may lead the doors to slide out of their tracks and damaging the entire set-up
5. Foldable or Folded Doors
A folding door is a type of door which opens by folding back in sections or so-called panels. They are made of narrow vertical strips or creases that fold back into a compact bundle.
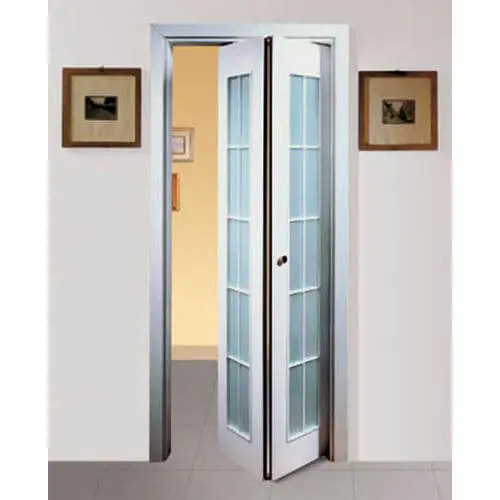

These strips/creases are will be hanged from the top, and run on a track. They save space as they do not swing out/in. They are preferable when the additional width is not available for installing a sliding door. However like sliding doors, foldable doors provide poor insulation. They are also noisy and considered poor in durability.
6. Collapsible Doors
These doors are made of vertical double channels (20X10X2 mm) joined together with hollows on the inside to create an artificial gap. These channels are spaced at 100mm – 200mm apart and braced with diagonal iron flats, which allow the shutter to open/close giving an appearance of a “steel-curtain”.
The shutter operates within two rails, one fixed to the floor and the other at the lintel. The rollers are mounted at top and bottom to give equivalent movement in both directions for easier operation.

These doors are generally provided for increased safety and protection to property and generally used in garages, workshops, public buildings etc
7. Rolling Shutters
These Shutters are generally used for shops/go-downs. This shutter acts as a curtain thus preventing protection against fire and thefts, wind and hails.
The shutter is made of Steel slabs called laths or slates which are around 1.25 cm thick interlocked with each other and coiled upon a specially designed pipe shaft called “drum” mounted at the top.
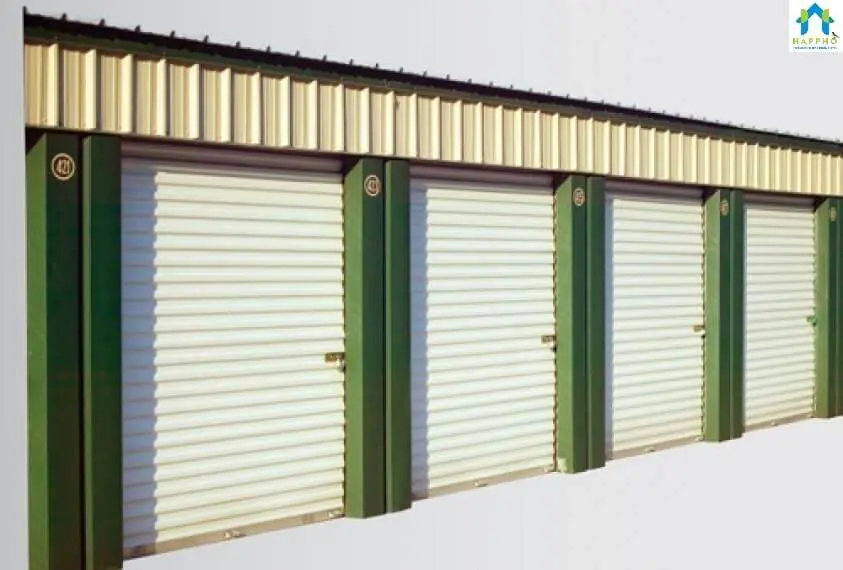

The shutter moves in two vertical steel guide channels mounted at the ends. The channels is made of steel sheets, deep enough to accommodate shutter and to keep it in position. A horizontal shaft and spring in drum allows shutter to be coiled in or out.
The door is raised to open it and lowered to close it. On large doors (more than 10 Sqm), the action may be motorized.
8. battened & Ledge Type
These doors consist of vertical boards called battens which are nailed or screwed to horizontal members called ledgers. The battens are generally 15 to 18 cm wide and 2 to 3 cm thick. Narrow Battened doors have a better appearance.

The above figure towards left is a battened and Ledged door to which braces are added to prevent sagging.
These Braces must slope upwards from hinge edge of the door as they are generally housed with a skew notch into the ledges.
9. Framed and Paneled
These doors consist of a frame made of stiles, top & intermediate rails. Into this a framework, a plywood panel is fitted, which will fit into a groove /rebate.
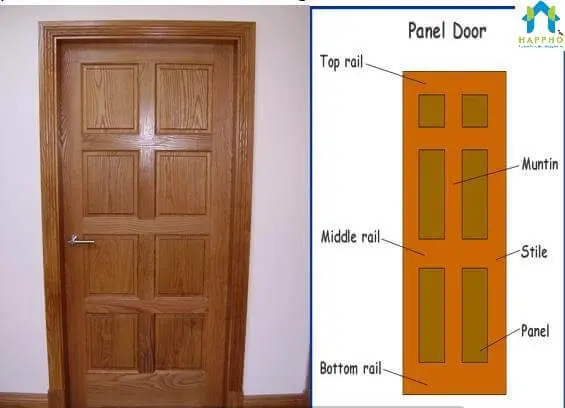
Usually, the panel is not glued to the frame but is left to ‘float’ within it so that seasonal movement of the wood comprising the panel does not distort the frame.
A. Glazed/Slash
These are same as framed/paneled doors, except one of the panels is replaced with a glass to improve visibility of the interior room.

Glazed/Slash door Wired Gauge door Louvered Door
B. Wire Gauge Door
In this door, the panel is replaced with a wire gauge to provide free air and also prevent mosquitos, flies, insects entering into the door building.
C. Louvered Door
In this door the panels are replaced by a series of lovers, permitting air ventilation, but guarantee privacy to those within.
10. Flushed Door
Flush doors have solid rectangular blocks of softwood on the inside arranged end to end as the frame , and covered on both side with a very thin layer of ply about 2.5 mm thick. These doors cannot be used where the door is exposed to rain as the wood may deteriorate rapidly.

– P. N. Aditya