A Building is any structure that is constructed to meet the needs and purpose of users. Residential / commercial / institution / educational / Assembly / Industrial / Storage etc. are some of types of building which are designed by an Architect / Structural designer and executed or constructed by Civil Engineer.
A building is combination of various components. A Civil Engineer should have good knowledge of execution of each and every component with respect to design layouts given by Architect.
-
How much cement,sand and water is required for 12mm Thick plastering????
-
which one is heavier, cement or sand??
Classification of Component Parts
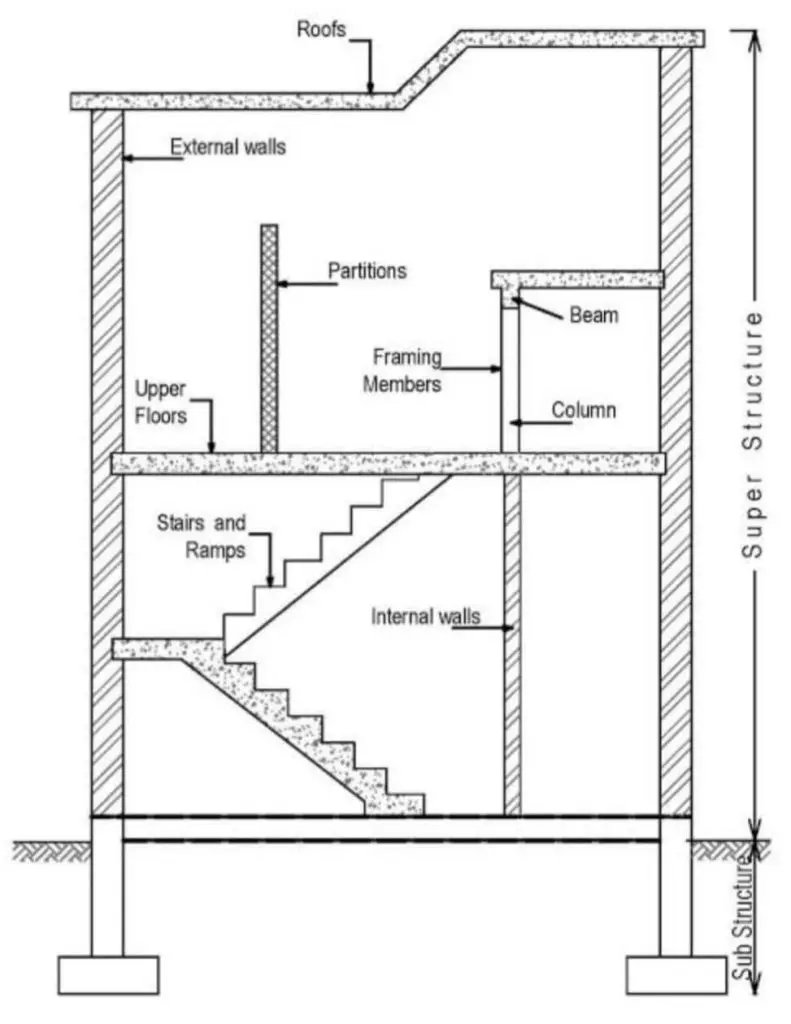
1. Substructure
It consists the parts of building below ground level. Function of sub structure is to transmit the load from super structure to the soil.
2. Plinth
It is connecting level between super and sub structure of building. Located immediately above ground level and below super structure.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6o3KqENrW5U
3. Super Structure
It is part of structure above ground level whose function is to serve the purpose of building.
-
Fire resistant properties of building materials.
-
6 types of brickwork defects due to poor workmanship
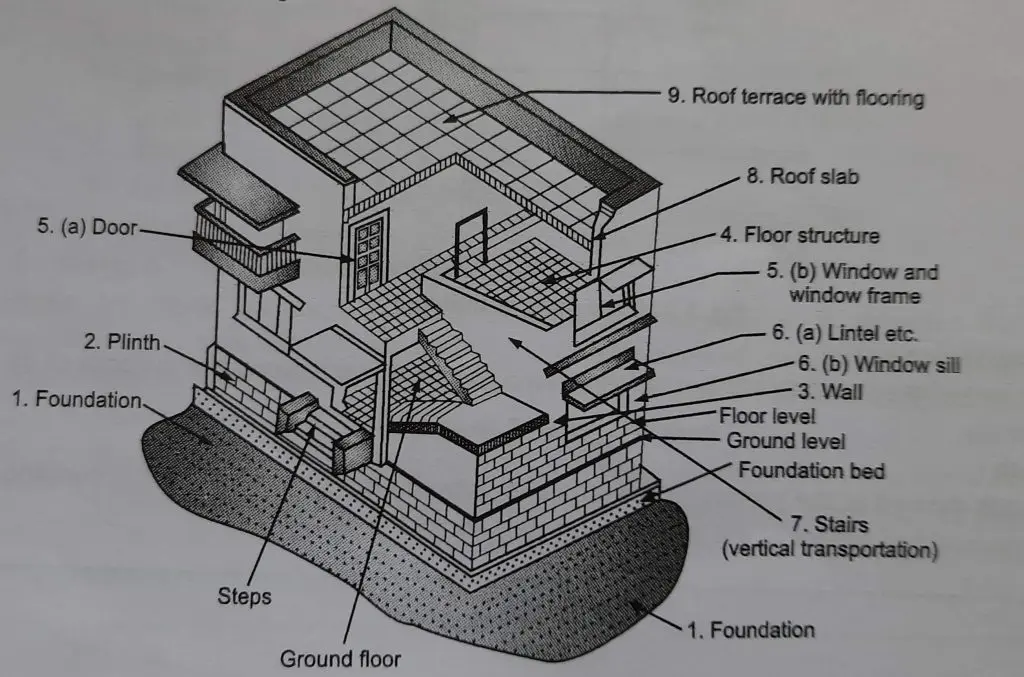
Components of Building
1. Foundation
It is part of sub structure forming the base is building . It’s function is to transfer the load from building to the soil. Also it resists / withstands seismic loads exerted by the soil.
Material used is steel bars and concrete along with filling material such as stones, clay bricks etc. It varies from type of structures / buildings . Shallow foundation is adopted for Load Bearing and RCC Structure.
2. Plinth
It is located between Foundation and Super Structure made up of damp proof course . It’s function is to control differential settlements, to connect all columns to foundations , to control leaking of water.
3. Walls and Columns
Coloumns
It is a vertical component which is erected from foundation to the top most portion of building . It’s main function is to carry the loads of super structure and transferring them to foundation (in a framed structure).
Columns are usually made up of reinforcement steel bars and concrete. In some cases, columns can be made of timber, structural steel and other materials also. Column comes in various shapes like circular, rectangle , square , hexagonal , etc. This depends on the structural design, aesthetics and internal design of the building.
walls
Walls are vertical components which act as partition between two spaces and form the outer limits of building. Its function is to separate spaces from each other internally and to cover all the external sides of the building.
In load bearing structures, walls also act as structural member and carry the weight of the building. This is then transferred to brickwork foundation done underneath the soil.
Walls can be constructed using various materials such as bricks (burnt clay / cement) , stones, AAC blocks, CLC blocks, Hollow or Solid Concrete blocks etc.,
Now a days the internal partition can be made using other materials also like plywood partitions, gypsum partitions
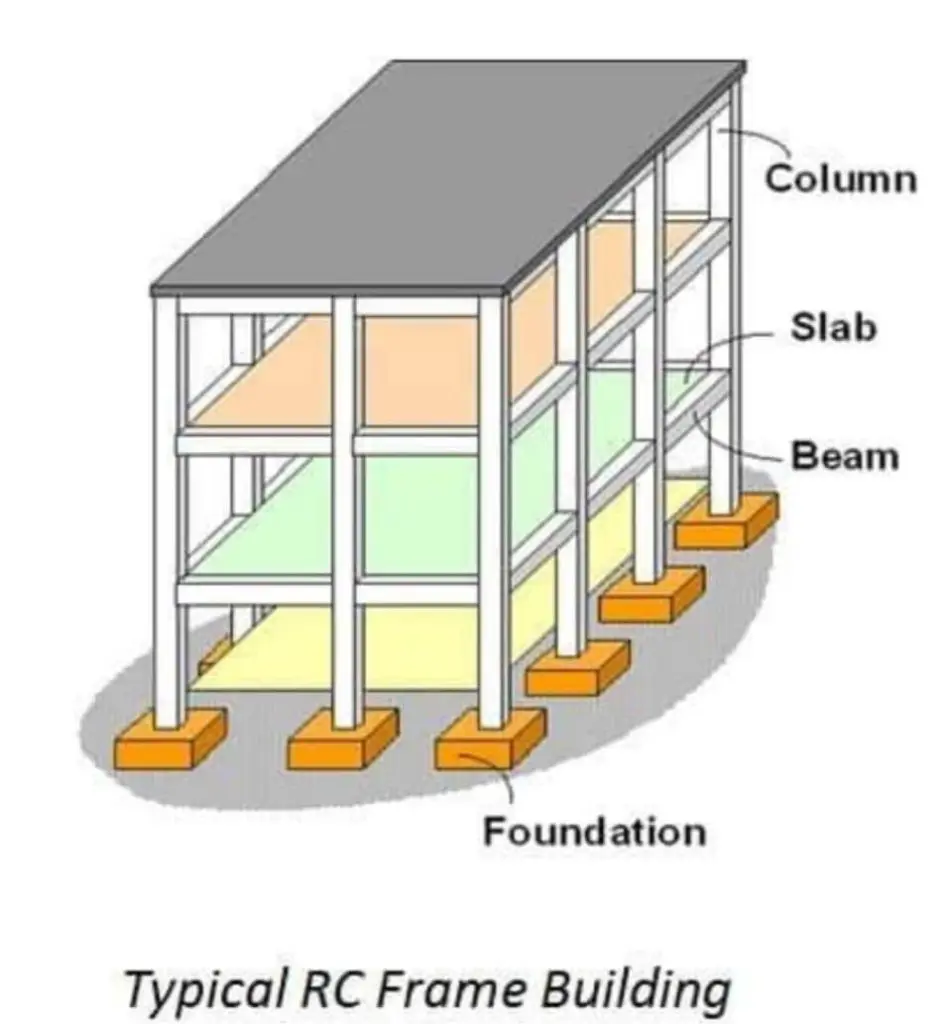
4. Roof Slab and beams
Roof Slab
Roof Slabs are horizontal structural member providing base to floor and ceiling to the users of adjacent storeys. Slab connects beams and columns. Also supports and distribute loads from beam and column . The lower portion of slab acts as ceiling and upper portion acts as floor between two adjacent storeys. Slab is made of material concrete and reinforcement steel bars.
Beams
Horizontal components of building which acts as structural members connecting columns and slab . It carries dead and live load from building and transfers to columns . Varies in sizes as per total loads acting on it . Made of reinforcement steel and concrete .
5. Flooring
Flooring is a finishing layer provided to the roof slab, which is a structural member and which separates two adjacent storeys from each other. The purpose of flooring is to provide even finish to the roof slab and ensure proper slope for drainage of water.
There are numerious materials available for flooring finishing. Materials such as tiles (vitrified, ceramic), granite, marble, special stones, wood, timber laminates, wooden flooring, brick flooring, etc.,
6.Doors and Windows
Doors
These are openings provided for entry or exit of users / occupants into different spaces inside a building. They play an important role in circulation of occupants from one room to another. Privacy of a space can be maintained by doors. It provides protection to interior of any space from exterior.
Doors are made up of many materials such as metal, wood, timber, etc., and are usually placed in a door frame made up of same material. The portion of brickwork above the doors and windows are usually supported below lintels beams placed on the top of them. So keeping doors and windows height at one level is recommended in buildings.
Window
These are openings provided for circulation of air and to get natural light inside spaces of buildings. Windows are generally provided on external walls only.
Windows can be shape is rectangular, circular or elliptical. Windows are usually have glass with a framing material on top of it. The framing material can be aluminium, wood, UPVC etc., In olden Indian Houses, people used to cover entire windows with wooden shutters.
7. Lintel and Window Sills
Lintels are small beams provided over openings (windows and doors). It’s function is to provide support to the wall above openings. Lintels are usually made up of reinforced concrete or wood so as to take the loads from above.
8. Stairs
Vertical component which joins adjacent storeys of building and provide circulation of humans as well as materials from one storey to another. Stairs are Located at centre or corner building. Stairs come in different types based on shapes and materials used.
Shapes – dog legged, circular, helix, semi circular, rectangular, square, double helix etc.,
Material – Metal, RCC (Steel and Concrete ) timber, wood, combination of timber and wood etc.,
9. Roof terrace with Flooring and Parapet
Topmost horizontal part of building roof which can be used as roof terrace with floor finishes. Water tanks, solar panels are installed in roof terrace.
Parapet is a wall with short height (up to 1.2 m.) provided on roof terrace boundaries for protection / safety of users.
Some Important Points to remember
- Walls and slab act as important structural elements in LOAD BEARING STRUCTURE. Thickness of walls is grater than that of RCC building walls, so, floor area is minimum in load bearing structures. Step footing is adopted.
- Columns, Beams, Slabs act as important structural elements in RCC buildings. These should not be disturbed or demolished as they form the skeleton of RCC structure and carry all the load. Thickness of wall in framed structure is less in comparison with the thickness of wall in load bearing structure. Internal wall can be removed if required in framed structures, only under supervision of an engineer.
- Along with staircase, LIFT also plays an important role in vertical circulation. Lift is mechanically driven element used in multi-storeyed building or high rise structures. Purpose of lift is to transfer humans/materials from one floor to another in very less time.
– Vrushali Pathak
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zIhxDGxzMik