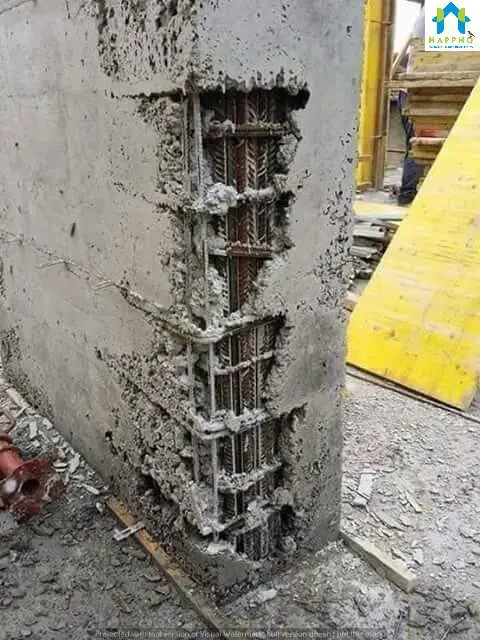
What is a honeycombing?
Honeycombing is a structural defect of a RCC Structure, areas of the concrete surface where the coarse aggregate are prominently visible are called honeycombed surface, giving a look of honey bees nest.
If not treated honeycombed surface, the RCC structure will not perform adequately as per its design (structurally weak), will also allow ingress of harmful agents like contaminated water and air through the created voids affecting durability of structure substantially.
They surface due to many reasons and demands immediate corrective and preventive actions.

Reasons for Honeycombing
Honeycombing in RCC Structure may occurs due to one or more of the following reasons
- Concrete mix not being cohesive.
- Concrete workability not sufficient/suiting its placement requirement.
- Insufficient compaction to concrete.
- Steel congestion not allowing concrete flow to all corner.
- Concrete already set before placing.
- High free fall of concrete ,while pouring
- Form work not watertight/rigid.
- Improper detailing and/or fixing of steel
how to Prevent Honeycombing in Concrete?
- All concrete batches to be cohesive, concrete production/cohesiveness should be periodically reviewed. Tip: If we are able to prepare “ball” out of the fresh concrete, we have a cohesive concrete mix.
- Concrete work ability should match the placement requirement, like a lightly reinforced column can have 75mm slump, a heavily reinforced column may require 150mm slump.

- Ensure proper compaction of placed concrete, vibrators to be removed as big air bubbles ceases to come out (over vibration will lead to bleeding). Different sizes (25mm, 40mm, and 60mm) of vibrator needle should be used as per RCC sections.
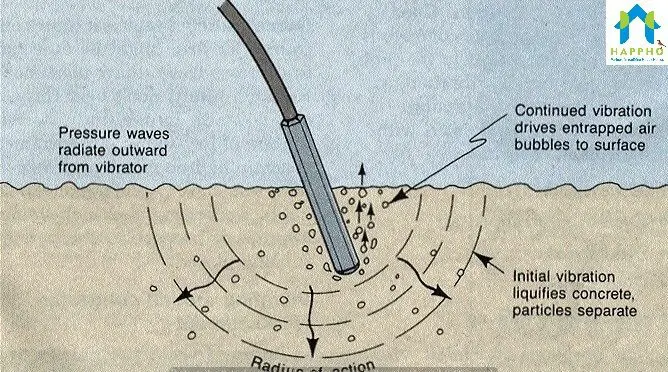
- Concrete should be thoroughly compacted and fully worked around the reinforcement, around embedded fixtures and into corners of the formwork. If care is not taken during vibration, it may result in honey combing,5 % Voids in Concrete, reduces strength of concrete by 30%.
- Cover to formwork, Pins and spaces bars to layers of reinforcement to facilitate proper compaction.

Steel Couplers can also reduce steel congestion
- Concrete should retain Slump before it is placed. Apart from initial slump, concrete should be designed to retain slump till the time it is placed
- Concrete fall should be kept minimum, if required concrete bucket with canvas pipes, concrete hose pipe, should be used to reduce concrete free fall height.

- Formwork need to be watertight, cement grout should not be lost while concrete placing.
- Steel detailing and fixing should be done to ease follow of concrete across all corners and depths. If steel congestion can’t be avoided special concrete formulations need to be recommended like self-compacting concrete, concrete with lower maximum aggregate size (12.5mm) etc.
Step by Step Procedure to Repair Honeycombed Concrete Surface
Step-1: Firstly, Remove the loose concrete particles (loosened aggregates and mortar) manually using a chipper and hammer and/or wire brush. Do not apply heavy force (like using breaker, electrical chipper etc.,) or else it would damage good virgin concrete in periphery.
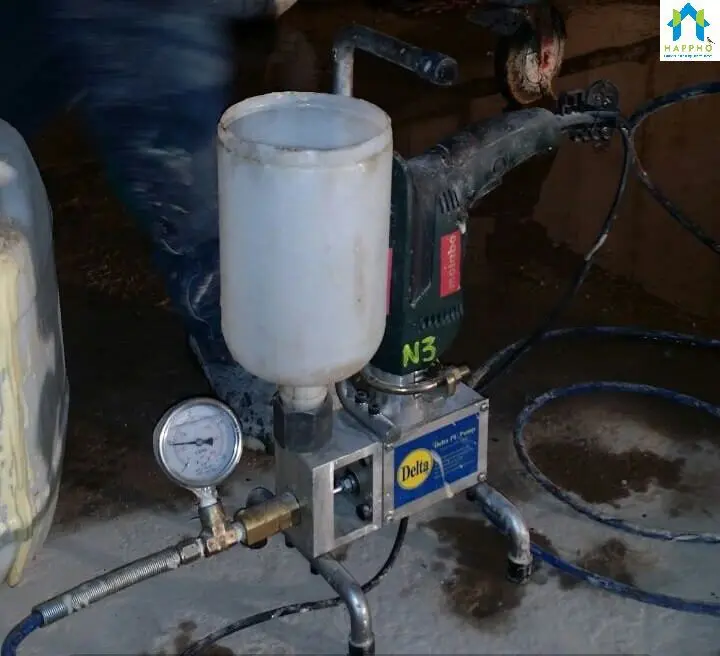
Step-2: Fix the packer on the honeycombed surface. Using mechanical Injection pressure pump, Grout the surface with non-shrink epoxy grout to fill the micro voids where repair mortar cannot reach.

Step-3: Post grouting apply self-curing repair mortar of equivalent compressive strength (Repair mortar are available in packaged ready made form in different strength grades). Note the buildup not to be more than 15mm thick.
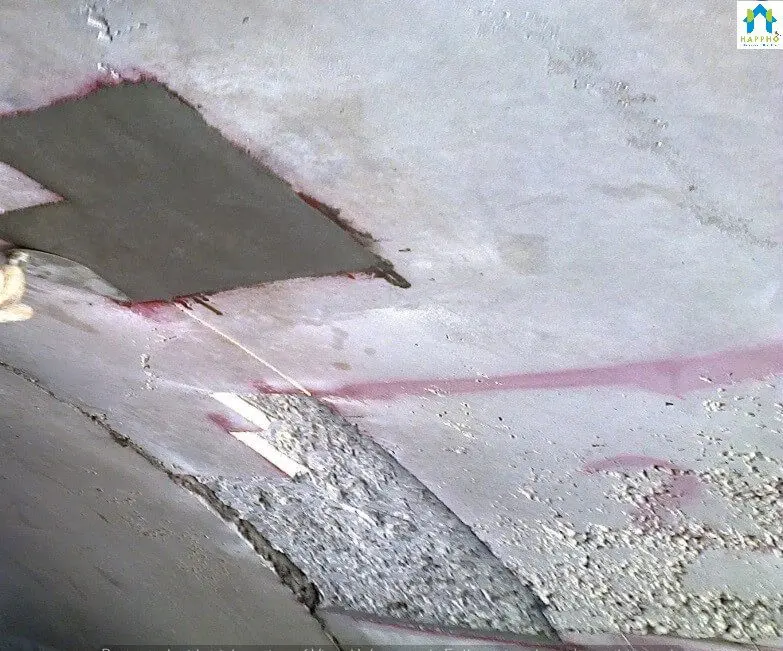

Comparison of Honeycombed surface with a repaired surface
Note: If the voids are large or hollow pockets are observed, then the same needs to be treated using micro concrete of equivalent grade (as the concrete used for RCC structure). Micro concrete are also available in readymade packages and in different strength grades.