Roofing is an important process while setting up a structure since it protects all the work done previously and provide them cover from the environmental disturbances, also making the inner environment sustainable. Since roofing is also an important part, people are always curious to know the various types of it and when to use what kind of roofing.
Roofs can be divided into many categories, for example according to size, material, shape, slope, thickness and so on. But all perform the same functions irrespective of the structural differences between them. But, what is a roof and what function does it perform??
Well, a roof can be defined as, in simple terms, a cover or a protective surface (thick and strong) used to protect the inner confined environment from dust, rain, temperature surges, and various other atmospheric or environmental disturbances.
Every structure has a roof according to its use or the structure itself (example roof of a stadium, roof of a hut or a house). Since roofing can be off different types, the materials used for it are also of various kinds, depending upon the strength or area (roofs at hilly regions are different from their counterparts at the plains).
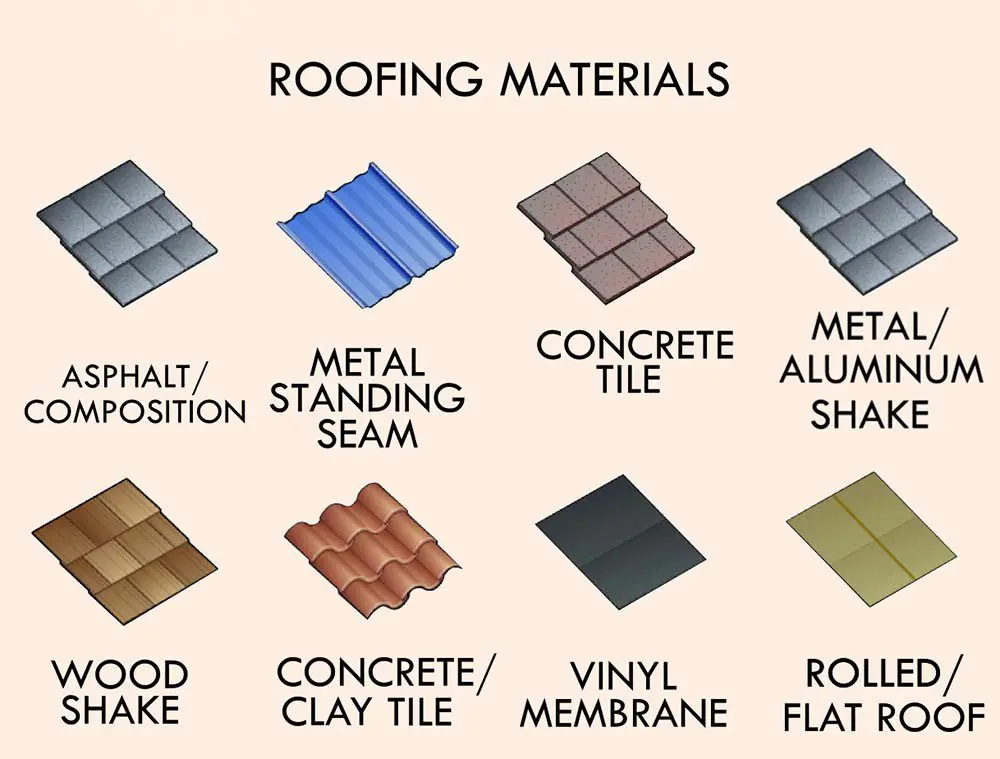

(Common Roofing Materials)
Apart from protection from water and other unwanted materials, it has also various purposes like :
- it must bear weight when necessary (e.g. Snow)
- must look attractive or suit the face of the structure
- must have permanent abrasion resistant finish
- must handle heat according to the climate ( no loss of heat in winters and no heat entrance in summers)
- providing insulation
- accommodating drainage pipes
It must be also made such that the load applied on it is evenly distributed and transferred to the load bearing components properly, to avoid collapse of roof.

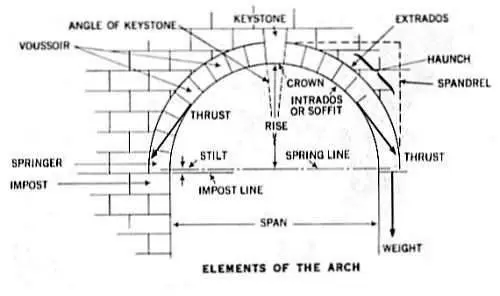
(Roofing Terminology)
Sloped roofs are those which makes an angle or a slope (a tilt), though every kind of roof has some slope (even flat roofs also have some slope to help in drainage). They are preferable when the structure is small, since putting them on a large house or a factory would turn them into a very costly affair. It also depends on the area and location, for example in hilly regions, they are more convenient since it prevents the cost of drainage systems and are long lasting there with respect to other kind of roofs. It is also used sometimes to provide aesthetic beauty, but other factors should also be looked upon before installing it since it has to support loads, and these qualities are more important than the aesthetics of the roof.
Types of Roofing Materials for Slopped Roofs
1. Thatch Roofs
They are used since the time immemorial and were used by the early human settlements. Since it was made by early humans, it comprised of dried grass, wood supports, and small degradable substances which they found useful for their purpose.
It generally makes an angle of 45 degrees or so (Shown in the image below). This thatch can be of desired thickness, but the support also should be designed accordingly to the load implied on it. This thatch also acts as a waterproof layer as when water falls on it, it comes down due to its slope.
These were developed around 735 A.D.
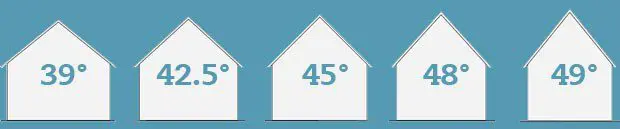
(Observe how slope change affects the kind of roof. Thatch roof is the one with 45 degrees)

(Notice how different layers act as a waterproofing material, and observe the supports)
Pros of Thatched Roof:
- Long Lasting:
A properly, professionally installed thatched roof which is maintained on a regular basis and sited away from any overhanging trees will offer great durability. You can expect thatch to last anywhere between 15 to 20 years in good condition. - Natural Insulation:
Being a naturally insulating material, thatch is able to insulate your home without the need for additional insulating materials in the loft space such as natural or synthetic wools. - Thatch darkens with age which helps it to blend with the surrounding area, creating a sense of harmony and belonging which more boldly coloured and textures tiles and slates cannot offer. This makes thatched roofs perfectly suited to more rural locations, although it is just as attractive in towns and villages.
Cons of Thatched Roof:
- Labor Intensive:
Installing a thatched roof is labor intensive as compared to the alternative roofing materials available.
- Highly Flammable:
Thatched roofs dry out and become highly flammable if not maintained properly.
- Higher Maintenance:
Thatched roofs must be regularly treated with fire-retardant, especially during the summer when the weather can cause thatch to become easily ignitable. The treatment of thatch is based on the impregnation of the material with a combination of biological preservative and fire retardant.
Recommendation
They are used when the budget is low. But, nowadays they are even being used by the People with high budgets since it gives the house more vintage and rustic looks. Suggested only for low cost construction purposes. Can be also used for temporary settlements.
Clay Roof
Clay tiles are used as a protective membrane. Clay is widely used because of its easy availability, and easy desired shape formation. They are durable and light weight, and offer better insulation when compared to their counterpart such as Ceramic tiles. These tiles work well and more efficiently when the roofs are sloped at 20 degrees or higher. As slope increases, efficiency and aesthetics increases. One of the most important considerations for installing clay tile is to have a great roofing underlay (Underlay is what lies beneath the tiles to provide support)
The most common type of clay tiles include:
- Slate: Thin rectangular sections of rock that come in varying sizes and thicknesses. (Rocks in clay tiles)
- Plain tiles: Small rectangular sections of clay with a smooth or sanded surface finish.
- Pantiles: A distinctive clay tile with an “S” shaped profile.
- Roman tiles: Similar to pantiles but with a cross-section that is flat with a small roll.

(A typical clay tiled roof. See how different tiles are joined and layered)
Pros of Clay Tiles
- Long Lasting:
Tile lasts a long time – its expected lifespan is greater than the lifespan of the material on which the roofing rests. - Fire and termite resistant:
Tile won’t rot or burn, and it can’t be harmed by insects. - Minimum Maintenance:
It requires little maintenance, and comes in a variety of colors, types, styles and brands.
Cons of Clay Tiles
- Heavy Material:
The biggest drawback to clay tile can be its weight. Depending on the material used to make it, tile can be very heavy – so heavy that extra roof support can be required. - Fading Color:
With some new materials, however, color is added only on the surface of the tile, and they can fade over time. Thus color only serves for short duration of time. - Fragile:
Tiles are fragile, so walking on them can break them. That makes it more difficult to accomplish maintenance like painting or cleaning rain gutters or fireplaces.
Recommended
They are advised to be installed only if you have a higher budget since it costs more than other roofing materials, and its installation can be a difficulty. Suitable for rural areas.
3. Slate/Stone Roof:
Slate is a fine grained rock obtained from sedimentary rock composed of volcanic ash and clay. Slate roofing tile has a long and storied history, and is generally known as one of the highest quality, longest lasting roofing materials on the market. Due to its usage in natural form, it is stronger than most of the other man made materials. It is finest grained foliated metamorphic rock (composed of several minerals like quartz, feldspar, graphite etc).

Pros of Slate/Stone Roofing
- Natural Look: Although slate is an expensive choice, it offers a very natural look and can be laid out in a variety of patterns.
- The benefits of slate are identical to those of tile: a very long lifespan, good fire protection, low maintenance, and an invulnerably to rot and insects.
- It comes in a good selection of sizes and colors, although colors are limited to those found in nature.
Cons of Slate/Stone Roofing
- Heavy Material: Like tile, slate can be very heavy, sometimes requiring expensive extra support.
- Fragile and Complicated to Work with: It, to, is breakable enough that walking on it is difficult for a non-professional, complicating such tasks as rooftop maintenance, gutter cleaning and painting.
- Expensive: Depending on thickness, grade and overall quality, its price can widely go up and can be costly to install.
- Though it is not ideal as it is heavy and has much of its self-weight acting on the supports. A roof with high self-weight is not recommended, since it also has to bear more loads and thus, overall load would become very high.
- This system is not highly waterproof as separate layers work as separate units and have no connection between them.
- To work properly, it must have an ideal slope of up to 30 degrees, to let water move away quickly. If the slope is lesser than that, then due to low speed of moving rainwater above the roof, the water will ultimately penetrate the layers and would fail to serve its purpose.
Recommendation
Recommended for? Villages or places where budget is a constraint. Also used in making up of churches, schools and similar kinds of structure etc. People nowadays have started using it in their Villas to give it a richer vintage look. It can also be used to give a structure a historic outlook.
4. Metal Roof
Since metal is easily available and because of its high strength, metal is used more commonly nowadays. It is used for nearly every type of building. It is strong, economical, waterproof, and can be used for any design. Steel is mostly used since it is alloyed and is safe from corrosion. These are thin sheets but are excellent regarding their purpose, and are stronger than many of the man-made and natural materials available.

(Steel sheets being used as a part of metal roofing)
pros of Metal Roofing
- Metal roofs are durable, fire retardant and almost maintenance-free.
- They are also energy efficient; metal reflects heat and blocks its transfer into the house.
- Can be easily cleaned.
Cons of Metal Roofing
- High installation costs
- Creates noise during the time of rain
Recommendation
Highly recommended for the roofing purposes. Also environment friendly since it is made up of recycled materials. Long life span and are strong, can bear almost any weight. Uncommon for houses in India but one may use this type of roof depending upon structure and location of the house. Modern constructors are giving it a high priority due to its overall strength and economy (with respect to its life expectancy).
Some of the other used roof types are as follows:
Conclusion
Roofs have modernised through times and have gone through multiple changes to serve the human needs. We can even have transparent roofs (Made up of glass) to have an outside view which can both be aesthetic and safe at the same time. Most of these roofs are durable for 100 years if properly maintained, but one should not use it after 50 years, and after this period, safety and inspection should be made regarding the quality and the loads acting over it. It must then be renovated or repaired according to further usage.
So considering the sloped roofs based on overall performance, Sloped roofs are suitable for smaller structures, since it would be expensive for large areas. Also they are installed depending upon regions. Installation costs are high but they tend to stay for years to come if properly maintained. Slope specific to each of its type should be maintained strictly otherwise it would not behave as an ideal roof and may fail to serve its use.